This guide provides a comprehensive overview of warehouse optimization, from core concepts and benefits to key processes, performance metrics, practical optimization tips, and future trends shaping modern warehouses.
What is warehouse optimization?
Warehouse optimization is the structured process of reviewing, redesigning, and continuously improving how a warehouse operates, stores inventory, and fulfills orders. The objective is to maximize operational efficiency while minimizing costs, errors, and wasted resources.

Warehouse optimization typically focuses on three interconnected dimensions:
1. Warehouse space optimization
This involves improving how physical space is utilized, including storage density, aisle width, racking configuration, and vertical space usage. Effective space optimization allows warehouses to increase capacity without expanding their footprint.
2. Process optimization
Optimizing workflows such as receiving, put-away, picking, packing, replenishment, and shipping helps reduce handling time, labor dependency, and operational bottlenecks. Well-designed processes ensure smoother material flow across the warehouse.
3. Technology and system optimization
Modern warehouse optimization relies heavily on digital tools such as warehouse optimization software and warehouse management systems (WMS). These systems provide real-time visibility, automate task allocation, and support data-driven decision-making.
Importantly, warehouse optimization is not a one-time initiative. It is an ongoing cycle of measurement, analysis, improvement, and validation, designed to keep warehouse operations aligned with changing business needs and customer demand.
The benefits of warehouse optimization
Better inventory management
Optimized warehouses maintain higher levels of inventory accuracy by combining structured storage strategies with real-time tracking systems. Accurate inventory data reduces stock discrepancies, improves replenishment planning, and minimizes excess safety stock.

Improved inventory management also supports better demand forecasting and reduces capital tied up in slow-moving or obsolete inventory.
Accurate order picking
Order picking is often the most labor-intensive and error-prone warehouse activity. Warehouse layout optimization, combined with effective slotting strategies, reduces picker travel time and minimizes picking errors.
As a result, warehouses achieve higher pick rates, lower return rates, and improved customer satisfaction.
Effective kitting and assembly
For warehouses handling kitting, bundling, or light assembly, optimization ensures components are stored logically and assembled efficiently. This reduces handling complexity and improves throughput during peak periods.

Fast shipping and receiving
Streamlined inbound and outbound processes shorten dock-to-stock and order-to-ship cycle times. Faster receiving ensures inventory becomes available sooner, while optimized shipping workflows support shorter delivery lead times.
Swift returns processing
An optimized reverse logistics process ensures returned goods are quickly inspected, sorted, restocked, or routed for disposal. This minimizes inventory loss and helps maintain accurate stock levels.
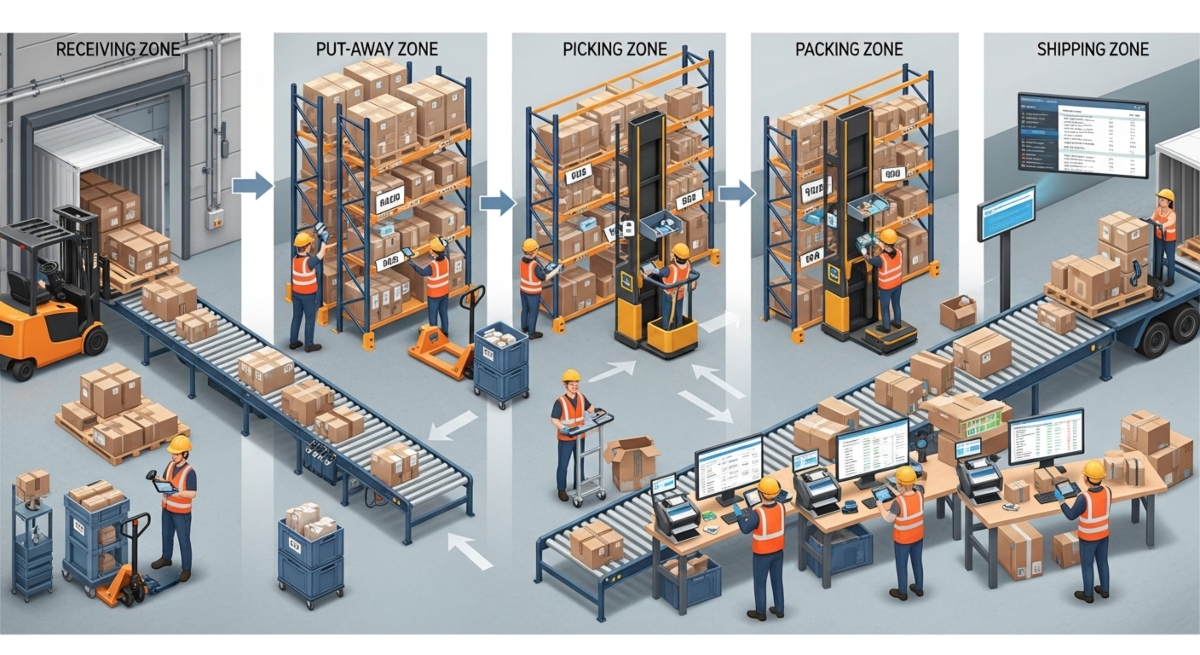
6 common warehouse processes
Understanding and optimizing each core warehouse process is essential for achieving end-to-end efficiency.
Receiving
Receiving includes unloading inbound shipments, verifying quantities, inspecting goods, and recording inventory in the system. Inefficient receiving can create congestion and delay downstream operations.
Optimization strategies include appointment scheduling, standardized inspection procedures, and barcode or RFID scanning.
Cargo put-away
Put-away involves moving goods from receiving to their designated storage locations. Optimized put-away rules consider product velocity, storage compatibility, and available space to minimize travel distance.
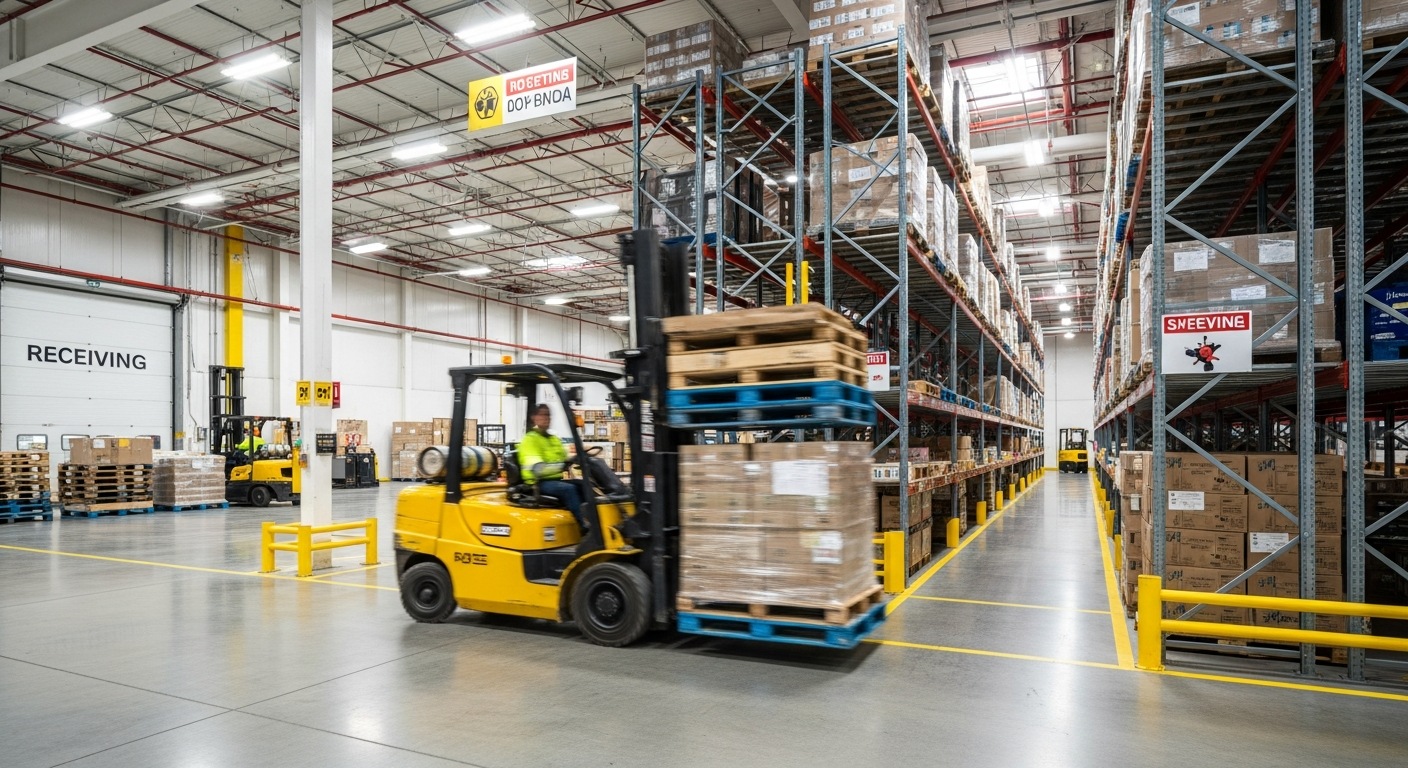

Storage
Storage optimization focuses on selecting the right storage method: pallet racking, shelving, bins, or floor storage; based on SKU characteristics, turnover rate, and handling requirements.
Picking
Picking methods such as batch picking, zone picking, or wave picking are selected based on order profiles and volume. Effective picking optimization significantly improves labor productivity.
Packing
Packing ensures orders are prepared securely and accurately for shipment. Optimization reduces packing errors, material waste, and handling time.
Shipping
Shipping includes order consolidation, labeling, carrier selection, and dispatch. Optimized shipping processes reduce delays and transportation costs while improving delivery reliability.
Key performance metrics for effective warehouse operations
Measuring warehouse optimization success requires clearly defined performance metrics.
Inventory accuracy
Inventory accuracy measures how closely system records match physical inventory. High accuracy reflects strong inventory control and process discipline.
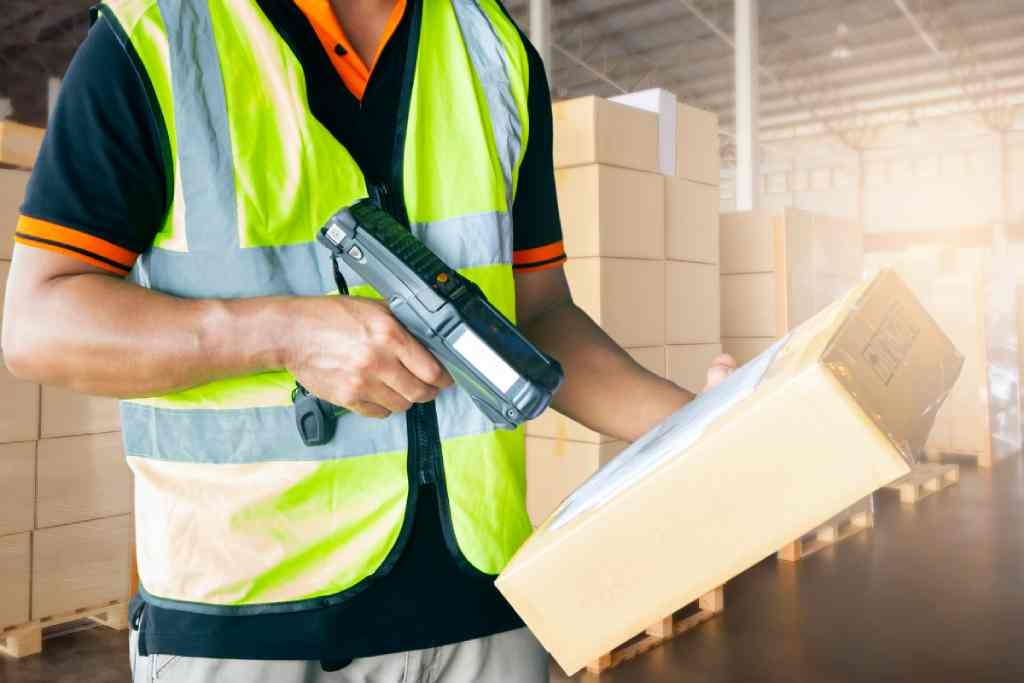

Order fulfillment rate
Order fulfillment rate tracks the percentage of orders delivered accurately and on time, directly impacting customer satisfaction.
Warehouse productivity
Productivity metrics such as items picked per hour or orders processed per shift indicate how efficiently labor resources are utilized.
Storage capacity utilization
Storage utilization shows how effectively available warehouse space is used and supports informed decisions about layout redesign or expansion.
Shipping and receiving efficiency
Metrics like dock-to-stock time and order cycle time measure inbound and outbound speed and reliability.
Cost per order
Cost per order captures labor, packaging, overhead, and system costs, helping assess the financial impact of optimization initiatives.
Tracking and analyzing KPIs
To leverage KPIs effectively, warehouse managers should:
- Establish baseline measurements
- Monitor KPIs consistently
- Analyze trends and performance gaps
- Identify root causes
- Implement corrective actions and measure results
8 tips for optimizing warehouse operations
Minimize the number of touches
Each additional handling step increases labor cost and the risk of errors or product damage. Reducing unnecessary touches through better put-away rules, cross-docking, and streamlined workflows helps improve speed and accuracy. This approach directly supports higher productivity and lower cost per order.
Balance capacity with efficiency
Maximizing storage density without considering workflow efficiency can slow down picking and material movement. A balanced warehouse layout ensures sufficient capacity while maintaining smooth traffic flow for people and equipment. This balance is essential for sustainable warehouse space optimization.
Invest in robotics
Robotics and automation improve consistency and throughput, especially in high-volume or repetitive tasks. Automated picking, sorting, and transport reduce dependency on manual labor and minimize human error. Over time, robotics help warehouses scale without proportional increases in labor costs.
Organize based on product velocity
Fast-moving SKUs should be stored closer to picking and shipping areas, while slow-moving items can be placed further away. This velocity-based organization reduces travel time and increases picking efficiency. It is a core principle of warehouse layout optimization.
Stock materials based on logical sequencing
Items that are frequently picked together should be stored near each other. Logical sequencing simplifies picking routes and reduces order processing time. This approach also supports more accurate and efficient kitting operations.
Automate shipping routing
Automated shipping rules select carriers and service levels based on cost, delivery speed, and destination. This reduces manual decision-making and shipping errors. As a result, warehouses achieve faster dispatch and more predictable delivery performance.

Align operations with business KPIs
Warehouse activities should directly support business goals such as order accuracy, delivery speed, and cost control. Aligning daily operations with KPIs ensures optimization efforts focus on measurable outcomes. This creates a clear link between warehouse performance and overall business success.
Use warehouse management software
Warehouse optimization software provides real-time visibility into inventory, labor, and workflows. A WMS helps standardize processes, automate task allocation, and track performance metrics. This technology foundation is critical for long-term warehouse optimization.
Step-by-step approach to warehouse optimization
- Assess your current warehouse layout and workflows
- Identify operational pain points and constraints
- Improve inventory accuracy before process redesign
- Implement or upgrade a WMS
- Apply Lean warehousing principles
- Train staff continuously
- Consider outsourcing to a 3PL when appropriate
Emerging trends and the future of warehouse management and optimization
Warehouse optimization is evolving rapidly due to technological advancement and changing customer expectations.
AI and advanced automation (robotics)
AI-driven systems predict demand, optimize slotting, and dynamically assign tasks. Robots and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) handle repetitive tasks, increasing speed and accuracy.

Internet of Things (IoT) and connectivity
IoT devices enable real-time tracking of inventory, equipment, and environmental conditions, creating intelligent and connected warehouses.
Cloud-based WMS, WES, and data analytics
Cloud platforms offer scalability and faster deployment. Advanced analytics support proactive decision-making and real-time operational adjustments.
Omnichannel fulfillment and micro-fulfillment
Unified inventory views and strategically located micro-fulfillment centers enable faster delivery across channels.
Read more: Omnichannel Fulfillment Explained: Meaning, Strategies & Top Providers for Retailers

Sustainability and green logistics
Energy-efficient infrastructure, renewable energy, and waste reduction initiatives are becoming essential components of warehouse optimization strategies.
Warehouse optimization FAQs
Common challenges and solutions in warehouse optimization
Challenges include limited space, labor shortages, inaccurate inventory, and inefficient layouts. Solutions involve warehouse layout optimization, automation, and better system integration.
How does shipping and returns management affect warehouse optimization?
Efficient shipping and returns reduce congestion, improve inventory availability, and lower costs, enhancing overall performance.
What role does technology play in warehouse optimization?
Technology enables automation, visibility, analytics, and scalability, making optimization sustainable long-term.
How can companies measure the success of warehouse optimization?
By tracking KPIs such as inventory accuracy, order fulfillment rate, productivity, space utilization, shipping efficiency, and cost per order.
How can I improve my warehouse performance?
- Track and analyze KPIs regularly
- Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- Continuously refine processes
- Invest in training and technology