Whether you are a small ecommerce startup or a rapidly scaling omnichannel brand, improving your order fulfillment process is no longer optional. This guide will help you understand what the order fulfillment process is, why it matters, the most common challenges businesses face and 10 practical strategies you can apply to build a scalable and efficient fulfillment operation.
What is order fulfillment process?
Definition of the order fulfillment process
The order fulfillment process refers to the complete sequence of steps a business follows after a customer places an order, from receiving that order to delivering the product to the customer and managing post-delivery activities such as returns.
In simple terms, it is how a business turns a confirmed order into a successfully delivered package. While fulfillment is often confused with shipping or logistics, it actually covers a broader scope that includes inventory management, order processing, picking, packing, delivery and reverse logistics.
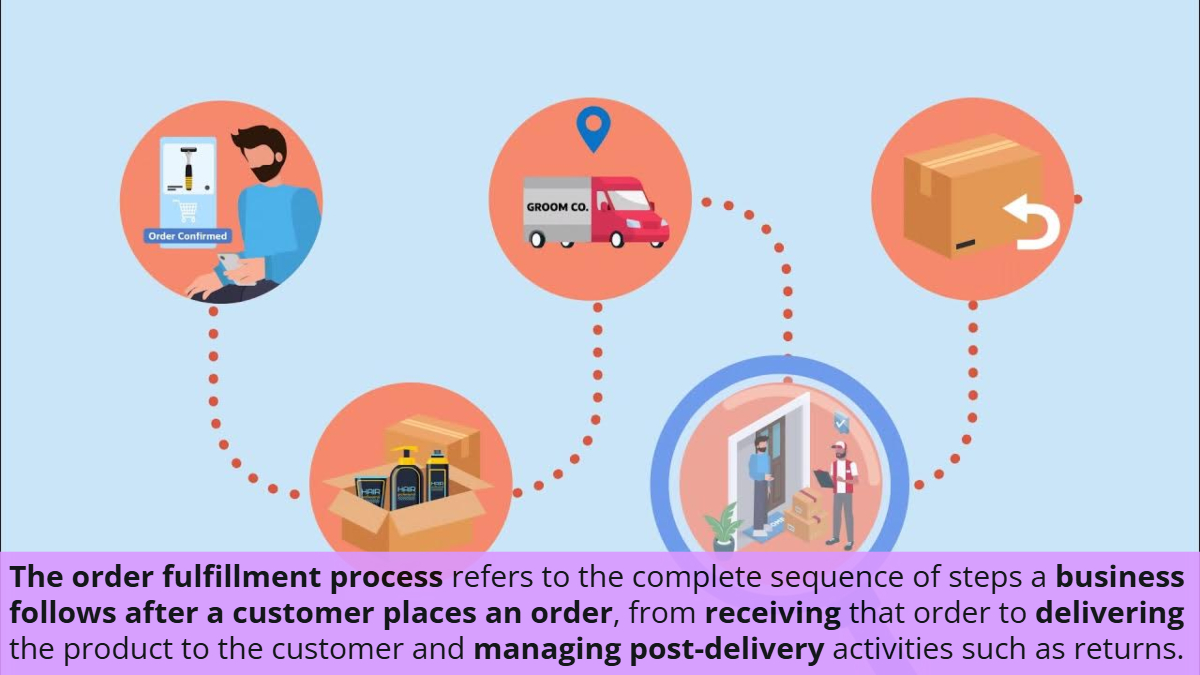
A well-designed order fulfillment process ensures that customers receive the right products, at the right time, and in good condition, while keeping operational costs under control.
Order fulfillment process steps explained
Although the exact workflow can vary by business model, most order fulfillment process steps follow a similar structure:
Order placement
A customer places an order through an ecommerce website, marketplace, or B2B sales channel.
Inventory confirmation
The system checks inventory availability to confirm that the ordered items are in stock.
Order processing
The order is routed to the appropriate warehouse or fulfillment center for handling.
Picking
Warehouse staff or automated systems retrieve the ordered items from storage locations.
Packing
Items are packed securely, labeled, and prepared for shipment.
Shipping and delivery
The order is handed over to a carrier and delivered to the customer.
Returns and post-delivery support
Any returns, exchanges, or customer inquiries are managed through reverse logistics and customer service.
Each of these steps must work together seamlessly to create a reliable and efficient fulfillment operation.
Order fulfillment process example
To better understand how this works in practice, consider a simple order fulfillment process example for an ecommerce brand selling fitness apparel:
A customer places an order on the brand’s website for a pair of running shoes. The ecommerce platform automatically syncs the order with the inventory management system, confirming that the item is available at a nearby fulfillment center. The order is then pushed to warehouse operations, where staff pick the shoes from storage, pack them in branded packaging, and generate a shipping label.

The package is collected by a carrier and delivered within two days. After delivery, the customer receives a confirmation email and tracking updates. If the shoes do not fit, the customer initiates a return, which is processed through the brand’s return system and restocked once received.
This example highlights how technology, inventory accuracy and logistics coordination all play a role in successful fulfillment.
What is the final step in the fulfillment process?
Many people assume delivery is the final step, but in reality, the final step in the fulfillment process is post-delivery management. This includes delivery confirmation, customer communication, handling returns, processing refunds or exchanges and gathering feedback.
An efficient final step ensures that customers feel supported even after their order arrives, which directly impacts repeat purchases and brand loyalty.
Why order fulfillment process matters
Impact on customer experience and brand trust
The order fulfillment process is one of the most visible parts of the customer journey. Customers may forgive a slightly higher price, but they are far less tolerant of late deliveries, damaged products, or incorrect orders.

Consistent and reliable fulfillment builds trust. When customers know they can rely on your brand to deliver what was promised, they are more likely to return and recommend your business to others.
Cost control and operational efficiency
Fulfillment inefficiencies often hide significant costs. Poor inventory management can lead to excess stock or stockouts. Inefficient picking and packing increase labor costs. Slow shipping raises carrier fees and leads to customer complaints.
By improving your order fulfillment process, you can reduce waste, optimize labor, and gain better control over shipping and warehousing expenses.
The importance of improving order fulfillment process for growth
As a business grows, fulfillment complexity increases. More SKUs, higher order volumes, additional sales channels and international customers all add pressure to existing systems.
Improving the order fulfillment process early allows businesses to scale without sacrificing service quality. It also creates a foundation that supports expansion into new markets, new channels, and new customer segments.
5 common challenges in the order fulfillment process
Inventory accuracy and stockouts
One of the most common fulfillment challenges is inaccurate inventory data. Without real-time visibility into stock levels, businesses risk overselling products or running out of inventory unexpectedly.
Stockouts not only delay fulfillment but also damage customer trust and reduce lifetime value. Effective inventory management is essential for seamless order fulfillment.
Slow shipping and high fulfillment costs
Customers increasingly expect fast and affordable shipping options, such as two-day or even same-day delivery. Meeting these expectations can be difficult, especially when shipping costs continue to rise.
Balancing speed and cost is a major challenge. Expedited shipping often improves delivery times but significantly reduces profit margins if not managed carefully.
Returns and reverse logistics complexity
Returns are an unavoidable part of ecommerce, particularly in industries such as fashion and consumer goods. Poorly managed returns processes lead to delayed refunds, inefficient restocking and higher operational costs.
A complicated or unclear return experience can quickly erode customer trust and discourage repeat purchases.
Scaling fulfillment during demand spikes
Seasonal peaks, promotional campaigns and viral demand can cause sudden spikes in order volume. Without a scalable fulfillment strategy, businesses may struggle to process orders on time while maintaining accuracy and quality.

Scaling too slowly leads to delays, while scaling too aggressively can increase costs and operational risk.
Omnichannel fulfillment challenges
Modern brands often sell across multiple channels, including ecommerce websites, marketplaces, B2B platforms, and physical retail stores. Each channel has unique fulfillment requirements.
Managing inventory, orders, and customer expectations across channels requires strong integration and coordination. Without it, businesses risk inconsistent experiences and fulfillment errors.
10 strategies to improve your order fulfillment process
Align fulfillment strategy with business size and order volume
Your fulfillment strategy should reflect the size of your business and the number of orders you handle each month. Small businesses with low order volumes and limited SKUs may find it more cost-effective to manage fulfillment in-house.
As order volumes increase, manual processes quickly become inefficient. Businesses should regularly assess current and projected order volumes to ensure their fulfillment setup can support growth without disruption.
Build a scalable fulfillment model early
Many businesses wait until fulfillment problems arise before making changes. A better approach is to plan for scalability early.

Consider when your current strategy will no longer be sustainable. This proactive mindset allows you to transition smoothly to more advanced systems, additional warehouses, or outsourced fulfillment partners when needed.
Optimize inventory management for real-time visibility
Accurate inventory data is the foundation of an effective order fulfillment process. Businesses should implement systems that provide real-time visibility into stock levels across all fulfillment locations.
This helps prevent stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and support more accurate purchasing and production decisions.
Integrate sales channels with fulfillment technology
Orders from all sales channels should flow automatically into your fulfillment operations. Manual order entry increases the risk of errors and slows down processing times.
Integrated technology ensures that as soon as an order is placed, it is ready for picking, packing, and shipping without unnecessary delays.
Choose fulfillment software that fits your tech stack
Fulfillment software should simplify operations, not complicate them. Look for solutions that integrate seamlessly with your ecommerce platform and marketplaces.
The right software enables you to manage orders, inventory, and shipping from a single system, improving efficiency and reducing operational friction.
Enable omnichannel fulfillment capabilities
Omnichannel fulfillment allows businesses to deliver a consistent experience across all sales channels. This includes synchronized inventory, centralized order management, and unified reporting.
Brands that invest in omnichannel fulfillment are better positioned to meet customer expectations and adapt to changing buying behaviors.
Optimize fulfillment location strategy
Where you store inventory and ship orders from has a major impact on delivery speed and cost. Shipping long distances increases transit times and carrier fees.
By strategically placing fulfillment centers closer to customers, businesses can reduce shipping zones, improve delivery times, and lower transportation costs.
Use multiple fulfillment centers to reduce shipping time and cost
Leveraging multiple fulfillment centers allows businesses to route orders to the nearest location. This approach increases the use of ground shipping, which is often faster and more affordable than expedited options.
It also provides redundancy, helping businesses maintain service levels during disruptions or demand spikes.
Prepare for international fulfillment and cross-border complexity
International fulfillment introduces additional challenges, including customs, duties, taxes, and longer delivery times. Businesses should carefully evaluate their international strategy before expanding.
Storing inventory locally within key markets or partnering with a global fulfillment provider can reduce complexity and improve customer satisfaction.
Balance customization needs with operational efficiency
Some products require special handling, customization, or packaging. While managing fulfillment in-house offers greater control, it may limit scalability.

The right fulfillment partner can support customization requirements while maintaining efficiency, allowing businesses to scale without sacrificing quality or brand experience.
Conclusion
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to improving the order fulfillment process. The most effective strategy depends on your business size, growth stage, product complexity, and customer expectations.
By understanding what the order fulfillment process is, addressing common challenges, and applying the strategies outlined in this guide, businesses can build a fulfillment operation that supports both customer satisfaction and sustainable growth.
Improving your order fulfillment process is not just about delivering products faster. It is about creating a reliable, scalable system that strengthens your brand and sets the foundation for long-term success.