This comprehensive guide explores both models, breaks down their operational mechanics, highlights key differences, and helps you decide which approach fits your business goals, budget, and risk tolerance.
Dropshipping vs wholesale: the key facts
At their core, dropshipping and wholesale represent two distinct distribution philosophies. Dropshipping is customer-centric, involving individualized shipments directly to end consumers from suppliers. Wholesale is volume-focused, moving large pallet loads to retail stores or distribution centers in bulk transactions.
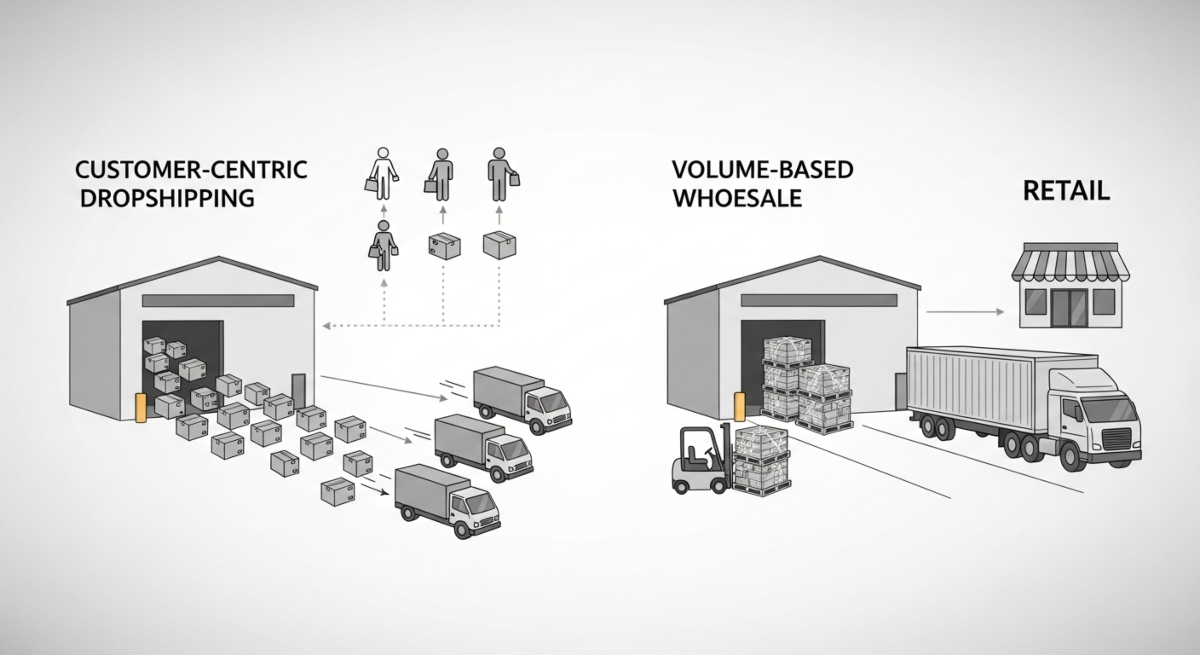
Dropshipping requires minimal upfront inventory investment, making it ideal for startups testing markets or launching new product lines. Wholesale demands substantial capital to purchase inventory in bulk, but offers superior per-unit costs and higher profit margins once scaled. The choice between dropshipping vs wholesale depends on your capital, operational capacity, and growth timeline.
How does the wholesale business model work?
Wholesale has been the traditional distribution method for centuries. Buyers purchase products in large quantities, typically in person from suppliers, manufacturers, or wholesale distributors. Orders are placed for entire pallets or container loads, which are shrink-wrapped and labeled with a single shipping label.

The wholesale process involves minimal personalization. Products arrive at retail stores, warehouses, or distribution centers where staff unload and organize them for resale. Buyers negotiate pricing based on order volume, with larger orders commanding lower per-unit costs. Once inventory is received, the wholesale buyer assumes full responsibility for storage, inventory management, and eventual retail sales.
Wholesale operations are streamlined from a logistics perspective. Pallets can be loaded within hours using minimal manpower, and shipments move to fewer locations. This efficiency translates to lower labor costs per unit shipped. However, wholesale requires significant working capital upfront to purchase inventory before generating any revenue.
How does the dropshipping business model work?
Dropshipping operates on an on-demand model. When a customer places an order through your ecommerce store, you purchase that specific item from a dropshipping supplier, who then ships it directly to the customer’s address. You never physically handle the product or maintain inventory.
The process begins when a customer orders from your online storefront. You receive the order details and payment, then immediately forward the order to your dropshipping supplier with the customer’s shipping address. The supplier picks and packs, then ships the item directly to the customer, often within 24 to 48 hours. You pocket the profit margin between your retail price and the dropshipping wholesale cost.

Dropshipping gained tremendous traction with the rise of ecommerce and accelerated dramatically during the COVID-19 pandemic. It allows entrepreneurs to launch online stores with minimal capital and test product-market fit before committing to wholesale inventory purchases. The model is inherently flexible, allowing you to add or remove products instantly without managing physical stock.
Main differences between dropshipping and wholesale
Holding stock
Wholesale requires you to purchase and store inventory. You assume responsibility for warehousing, insurance, and inventory management. Products sit in your facility until sold, tying up capital and space.
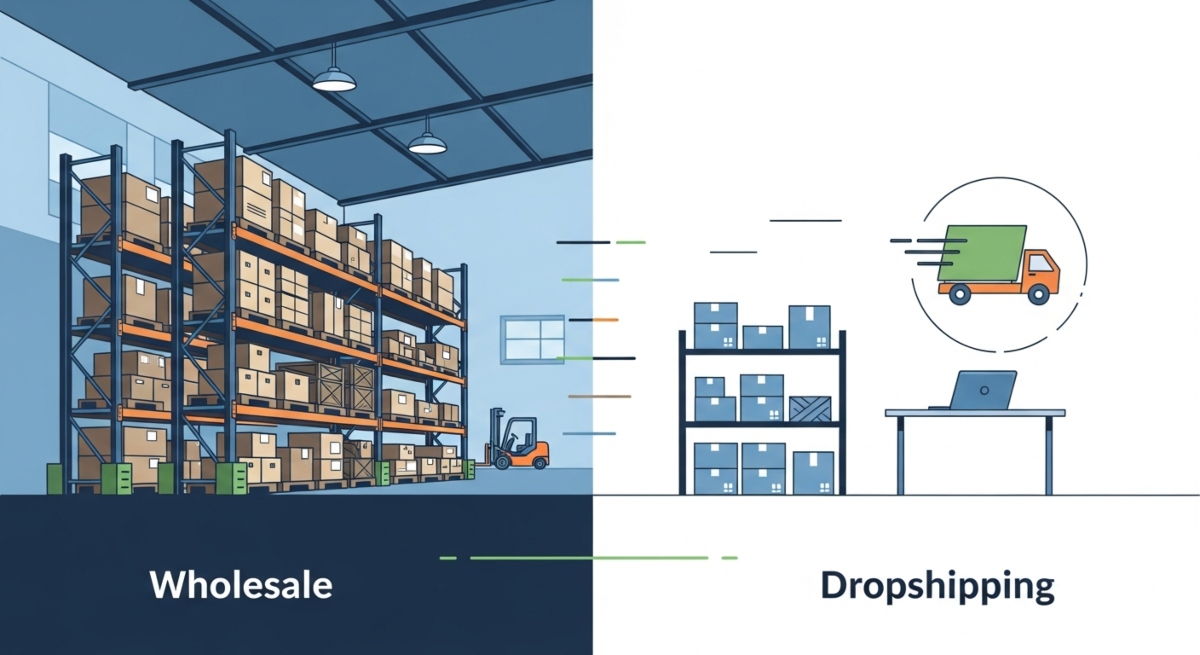
Dropshipping eliminates this entirely. Your supplier holds inventory, and you only purchase items after customers place orders. This fundamental difference shapes cash flow, warehouse costs, and business scalability.
Packing and shipping
Wholesale shipments are standardized. Pallets arrive shrink-wrapped with minimal labor required for unloading and organization. Dropshipping requires individualized packaging and labeling for each order.
Each package is customized with your branding, the customer’s address, and specific shipping labels. This labor-intensive process demands careful coordination across thousands of separate shipments to different geographic locations.
Starting supplies
Wholesale requires substantial starting supplies. You must invest in warehouse space, shelving, packaging materials, handling equipment, and labeling systems before selling a single unit.
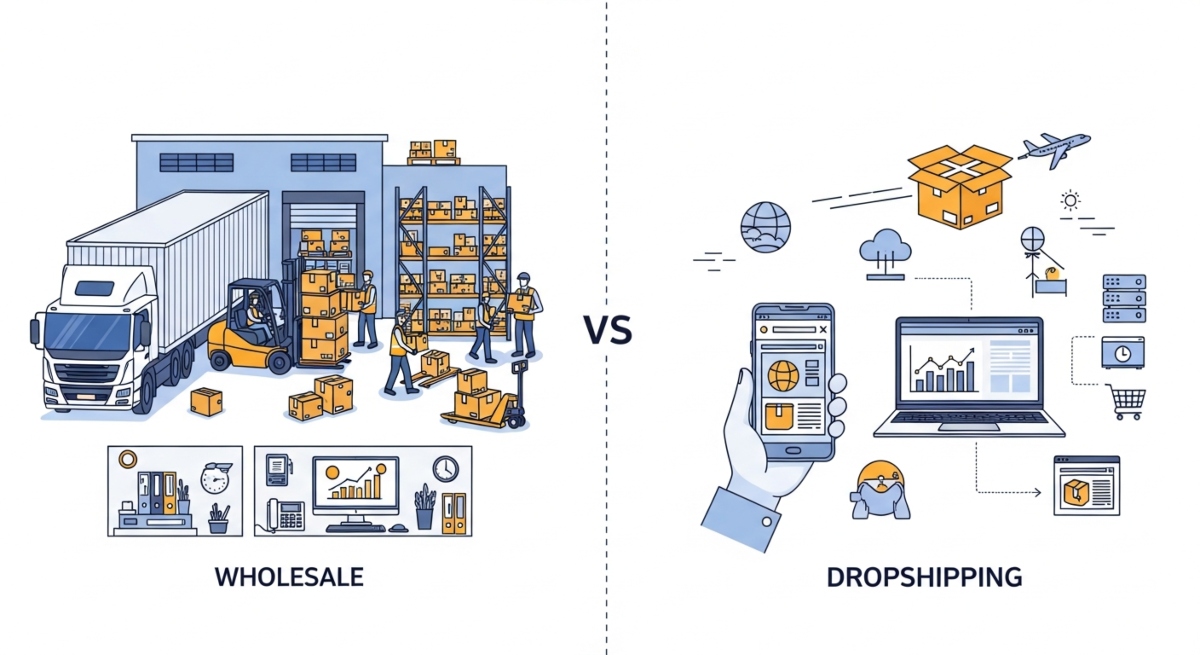
Dropshipping requires minimal starting supplies. You need an ecommerce platform, basic supplier agreements, and product listings. No physical warehouse is necessary.
Startup costs
This is a critical differentiator. Wholesale startup costs are substantial. A typical wholesale business requires $5,000 to $50,000+ in inventory purchases, warehouse deposits, handling equipment, and operational setup.
Dropshipping requires just $300 to $2,000 to launch an ecommerce store, create product listings, and establish supplier relationships. This cost advantage makes dropshipping accessible to entrepreneurs with limited capital.
Scaling and white-labeling
Wholesale allows white-labeling, where manufacturers customize packaging with your brand, creating a proprietary product line. You build brand differentiation through exclusive inventory. Dropshipping limits white-labeling options.
Most suppliers ship generic packaging, and white-label alternatives cost significantly more. Your brand identity depends primarily on your storefront and marketing rather than product exclusivity.
Supplier location
Wholesale traditionally involved in-person supplier relationships and local or regional sourcing. Modern wholesale has globalized, but physical negotiations and facility visits often occurred.
Dropshipping is inherently digital. You find suppliers online, negotiate via email or chat, and never meet them in person. This enables access to global suppliers but introduces quality control challenges.
Product exclusivity
Wholesale offers product exclusivity. Suppliers often grant exclusive distribution rights within specific geographic areas or customer segments. You build competitive advantage through exclusive inventory.
Dropshipping offers minimal exclusivity. Dozens of competitors can dropship the same products, creating intense price competition and commoditization.
Returns and refunds
Wholesale returns require reverse logistics coordination. Customers return items to your retail location or you manage returns at a warehouse facility. You then handle restocking, refurbishment, or return shipping to the supplier.
Dropshipping complicates returns. You must coordinate with customers, obtain returned items, repackage them, and ship them to your supplier’s returns department. This complexity often frustrates customers and strains relationships with suppliers.
Pros and cons of wholesale and dropshipping
Wholesale advantages
Wholesale offers superior per-unit costs, enabling higher profit margins. Buying 1,000 units costs far less per unit than buying 100 units or single items. Once you establish supplier relationships, you gain product exclusivity, white-labeling opportunities, and stronger brand identity.
Wholesale operations are streamlined from a fulfillment perspective, requiring less labor per unit shipped. You also build long-term supplier partnerships, enabling negotiation of better terms as volume increases.
Wholesale disadvantages
Wholesale demands substantial upfront capital. You purchase inventory before confirming customer demand, risking dead stock and cash flow challenges. Scaling requires investing in larger warehouse facilities, hiring fulfillment staff, and managing complex inventory across multiple locations.
Wholesale less suitable for testing new products or pivoting quickly. If a product underperforms, you’re stuck with unsold inventory. Wholesale also requires more operational complexity, including inventory forecasting, storage management, and handling reverse logistics.
Dropshipping advantages
Dropshipping requires minimal capital, making it ideal for startups and entrepreneurs with limited budgets. You test products without risking inventory investment. Adding new products is instant and risk-free.
You scale without managing warehouses or hiring fulfillment staff. Dropshipping offers flexibility to pivot quickly if products underperform. You focus primarily on marketing and sales, outsourcing logistics to specialists.
Dropshipping disadvantages
Dropshipping offers minimal profit margins. You pay wholesale prices for each unit sold, and after platform fees, marketing costs, and payment processing, margins often fall to 15-30%. You have limited product exclusivity. Competitors dropship identical products, driving prices down through competition.
Quality control is challenging. You depend on supplier reliability, packaging standards, and shipping speeds you can’t directly control. Customer service becomes complex. Returns require coordination with suppliers, and shipping times often disappoint customers accustomed to fast fulfillment.
Main differences between dropshipping and wholesale at a glance
| Aspect | Dropshipping | Wholesale |
|---|---|---|
| Startup Capital | $300-2,000 | $5,000-50,000+ |
| Inventory Holding | No | Yes |
| Per-Unit Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Profit Margins | 15-30% | 40-70% |
| Operational Complexity | Simple (early stage) | Complex |
| Fulfillment Time | 3-7 days | Immediate |
| Product Exclusivity | Low | High |
| Scalability | High flexibility | Requires infrastructure |
| Return Management | Supplier-dependent | Your responsibility |
| White-Labeling | Limited | Extensive |
| Best For | Startups, testing | Established businesses |
Questions to ask yourself before deciding on wholesale or dropshipping
Before committing to either model, answer these critical questions honestly:
Do I have $5,000+ in startup capital? If yes, wholesale becomes viable. If no, dropshipping is more accessible. How quickly do I need to generate revenue? Dropshipping launches faster. Wholesale requires months to establish supplier relationships and receive initial inventory.
Am I comfortable with thin margins initially? Dropshipping offers lower margins but faster launches. Wholesale demands patience to build but offers better long-term profitability. Do I want to build a branded product line? Wholesale enables white-labeling and exclusive products. Dropshipping limits brand differentiation.
How much operational complexity can I handle? Dropshipping requires marketing focus and customer service skills. Wholesale demands logistics expertise, inventory forecasting, and warehouse management. What’s my risk tolerance? Dropshipping minimizes financial risk. Wholesale risks inventory investment if products underperform.
Do I have existing supplier relationships? Pre-existing wholesale connections make that model easier. New entrepreneurs typically start with dropshipping. How important is customer fulfillment speed? Wholesale enables same-day or next-day fulfillment. Dropshipping typically requires 3-7 days.
5 key differences between dropshipping vs wholesale in operational complexity
Inventory management
Wholesale requires active inventory forecasting, purchase ordering, stock monitoring, and storage optimization. You track SKUs, monitor stock levels, and reorder before inventory runs out. Dropshipping eliminates this entirely. Your supplier manages all inventory.
Supplier relationships
Wholesale often involves long-term partnerships with dedicated account managers, negotiated pricing, and volume commitments. Dropshipping relationships are transactional. You order products on-demand with minimal negotiation.
Capital requirements
Wholesale ties up capital in inventory from day one. Dropshipping only costs money after customers place orders. This fundamental difference shapes cash flow and financial risk.
Packaging and fulfillment
Wholesale focuses on efficient bulk handling. Dropshipping emphasizes individualized packaging, custom inserts, branded materials, and personalized touch points. Dropshipping fulfillment is more labor-intensive.
Quality control
Wholesale allows you to inspect inventory upon arrival and establish quality standards directly with suppliers. Dropshipping depends on supplier quality, and quality issues are discovered after customers receive products.
When to choose dropshipping
Choose dropshipping if you’re launching your first online business with limited capital. Dropshipping is ideal for testing product ideas before committing to wholesale inventory. It’s perfect for entrepreneurs wanting to focus on marketing and sales rather than logistics. Dropshipping works well if you want rapid time-to-market and flexibility to pivot quickly. It’s suitable if you have limited warehouse space or prefer outsourcing fulfillment.
Dropshipping also makes sense if you operate in seasonal markets or niches where demand fluctuates significantly. You can scale product offerings up or down instantly without inventory risk.
When to choose wholesale
Choose wholesale if you have sufficient startup capital and want to build a long-term, scalable business. Wholesale is ideal if you’ve validated product demand and are ready to commit inventory investment. It’s perfect if you want exclusive products, white-labeling opportunities, or proprietary product lines.
Wholesale works well for established businesses scaling to higher volumes. It’s suitable if you already manage warehouse operations and have fulfillment expertise. Choose wholesale if you want superior profit margins and can manage inventory forecasting and returns logistics.
Can you combine dropshipping and wholesale?
Yes, and many successful businesses do. A hybrid approach balances the flexibility of dropshipping with the profitability of wholesale. For example, best-selling products transition to wholesale purchases for higher margins, while slower-moving or seasonal items remain on dropshipping. This approach lets you test products with dropshipping, then commit to wholesale once demand is validated.
The hybrid model requires managing two separate supplier relationships and operational workflows, adding complexity. However, it optimizes profitability by using each model where it fits best. Startups typically begin with 100% dropshipping, then shift 30-50% of revenue to wholesale as they grow.
Frequently asked questions about dropshipping vs wholesale
What is the main difference between dropshipping and wholesale? The primary difference is inventory holding. Wholesale requires you to purchase and store inventory in bulk before selling. Dropshipping eliminates inventory. You only purchase items after customers place orders, and suppliers ship directly to customers.
Which is more profitable: dropshipping or wholesale? Wholesale is more profitable per unit once scaled. Per-unit costs are 40-60% lower, enabling profit margins of 40-70%. Dropshipping margins typically fall to 15-30% after all costs. However, dropshipping requires less capital and launches faster, so it may generate faster absolute profits initially.
Which model is easier for beginners: dropshipping or wholesale? Dropshipping is easier for beginners. It requires minimal capital ($300-2,000 vs $5,000-50,000+), no warehouse management, and faster market entry. Wholesale demands more operational expertise, capital, and patience but offers better long-term economics.
Which model has better customer satisfaction? Wholesale typically offers superior customer satisfaction due to faster fulfillment (same-day or next-day vs 3-7 days). However, dropshipping satisfaction depends on supplier speed and quality. Premium dropshipping suppliers can compete with wholesale fulfillment.
How do startup costs compare? Dropshipping startup costs are 5-10 times lower than wholesale. Dropshipping requires $300-2,000 for a platform, domain, product listings, and initial marketing. Wholesale requires $5,000-50,000+ for inventory purchase, warehouse deposits, equipment, and operational setup.
Can I transition from dropshipping to wholesale? Yes, many businesses start with dropshipping for validation, then transition to wholesale as demand grows. This hybrid approach minimizes risk and maximizes profitability. The transition requires establishing wholesale supplier relationships and securing capital for inventory.
Conclusion
Dropshipping and wholesale serve different purposes at different business stages. Dropshipping is ideal for startups testing markets with minimal capital and maximum flexibility. Wholesale suits established businesses prioritizing profitability, exclusivity, and operational efficiency over speed-to-market.
The best choice depends on your capital availability, operational expertise, risk tolerance, and timeline. Many successful ecommerce businesses combine both models, using dropshipping for product testing and wholesale for high-demand items. Start with the model matching your current circumstances, then evolve your strategy as your business grows and your circumstances change.
Ready to launch your ecommerce business? Begin by evaluating your capital, timeline, and operational capacity. If you’re bootstrapping with limited funds and want rapid market entry, start with dropshipping. If you have capital and want to build a proprietary brand, begin wholesale sourcing. Most importantly, stay flexible and willing to evolve your model as your business matures.