This guide explains what is B2B fulfillment, how it differs from B2C fulfillment, key components of the process, best integration practices, and practical ways to improve fulfillment performance at scale.
What is B2B fulfillment?
B2B fulfillment refers to the process of storing, managing, and shipping products from a business to another business rather than directly to consumers. Typical recipients include retailers, distributors, wholesalers, franchise locations, or corporate buyers.

Unlike direct-to-consumer fulfillment, B2B order fulfillment often involves large order quantities, recurring purchase cycles, strict compliance requirements, and predefined delivery windows. Orders are frequently palletized, shipped in bulk, and governed by service-level agreements (SLAs).
Modern b2b fulfillment services are increasingly supported by technology, including warehouse management systems (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) integrations, and electronic data interchange (EDI), enabling businesses to automate complex workflows and scale efficiently.
5 key components of the B2B fulfillment process
A successful B2B fulfillment operation relies on tightly coordinated processes that prioritize accuracy, compliance, and reliability over speed alone.
Order processing
Order processing in B2B environments is often more complex than in B2C. Orders may arrive through EDI, ERP systems, purchase orders, or long-term contracts rather than simple ecommerce checkouts.
B2B order fulfillment systems must validate order details, pricing agreements, minimum order quantities, delivery schedules, and retailer-specific requirements before fulfillment begins. Automation is essential to reduce manual errors and processing delays.
Inventory management
Effective inventory management is foundational to scalable b2b fulfillment. Inventory is typically managed in bulk units such as cases or pallets and may be allocated across multiple sales channels.
Advanced inventory systems provide real-time visibility, support demand forecasting, and prevent overselling or stockouts. This level of control is especially critical for businesses handling recurring wholesale orders or seasonal demand spikes.
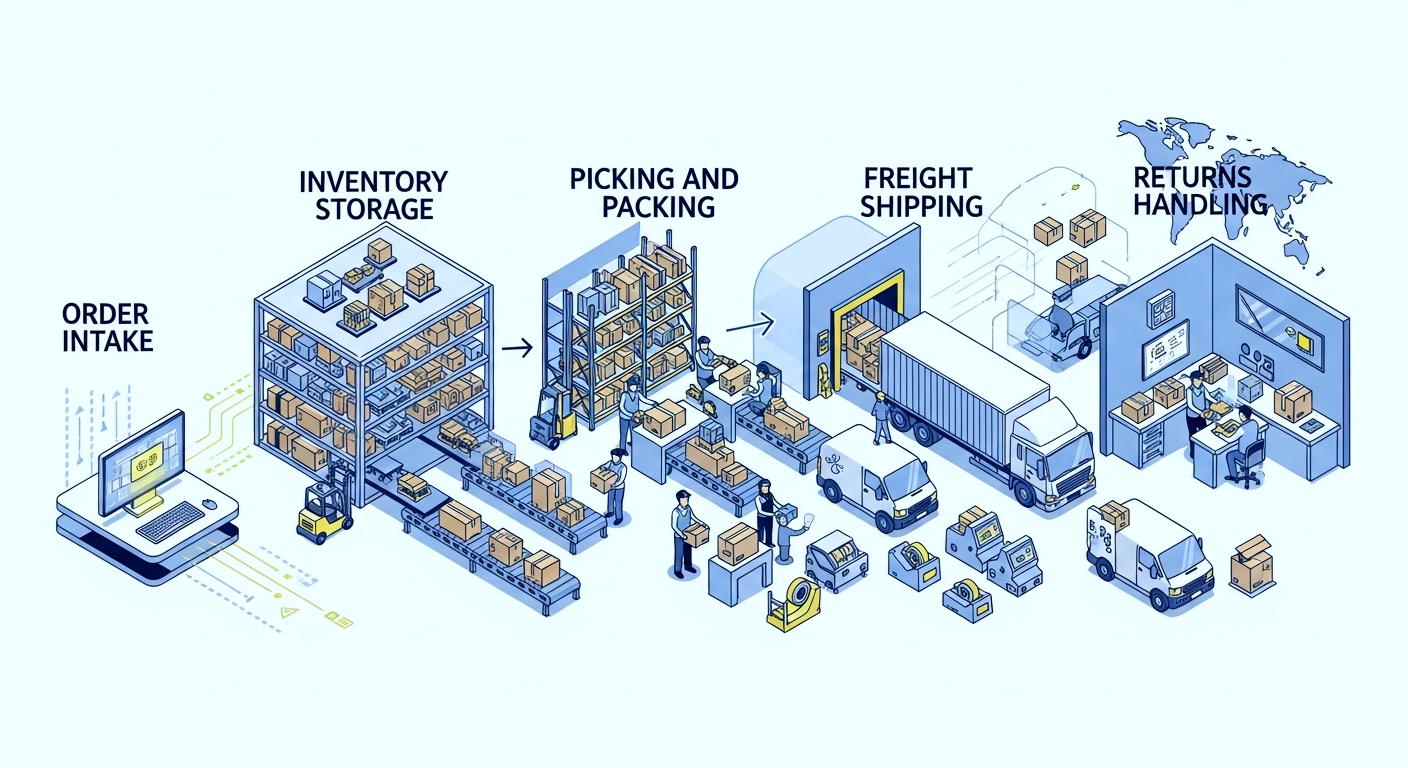
Picking and packing
B2B picking and packing focuses on efficiency and compliance rather than customization. Orders often involve full cases or pallets, requiring optimized warehouse layouts and handling equipment.
Packing must meet retailer and carrier standards, including labeling formats, pallet configurations, and documentation accuracy. Errors at this stage can result in chargebacks, rejected shipments, or delayed payments.
Shipping and delivery
Shipping in B2B fulfillment typically involves freight carriers rather than parcel services. Common methods include LTL (less-than-truckload), FTL (full truckload), and regional freight networks.
Delivery scheduling, dock appointments, and carrier coordination are critical. Businesses seeking the fastest order fulfillment for B2B retailers must balance speed with cost efficiency and compliance.
Returns management
While returns are less frequent in B2B than B2C, they are often more complex. Returned goods may require inspection, refurbishment, restocking, or disposal according to contractual agreements.
A structured returns management process protects inventory value and maintains strong relationships with retail partners.
When to outsource to a B2B fulfillment provider
Not every business starts with outsourced fulfillment, but growth often makes it necessary.
In-house fulfillment challenges
Managing B2B fulfillment internally can strain resources as order volume increases. Common challenges include limited warehouse space, labor inefficiencies, technology gaps, and difficulty meeting retailer compliance requirements.

When fulfillment costs rise faster than revenue, outsourcing becomes a strategic decision rather than an operational one.
Expansion into wholesaling
Brands expanding from DTC into wholesale often underestimate the complexity of B2B fulfillment. Retailers demand consistent delivery performance, accurate documentation, and strict adherence to routing guides.
Outsourcing to specialized B2B fulfillment services helps brands enter wholesale channels without rebuilding their logistics infrastructure.
Meeting retailer requirements
Large retailers impose detailed fulfillment standards, including EDI transactions, labeling rules, packaging specifications and delivery windows. Failing to meet these requirements can result in penalties or loss of contracts.
A B2B fulfillment partner experienced in compliance reduces risk and protects revenue streams.
B2B fulfillment vs B2C fulfillment: how they’re different
Understanding the distinction between B2B and B2C fulfillment is essential when designing logistics operations.

Order and unit volume
B2B fulfillment handles fewer orders with significantly higher unit counts. A single order may represent hundreds or thousands of units.
B2C fulfillment processes high volumes of small, individual orders with low unit counts.
Shipping methods
B2B fulfillment relies on freight shipping, pallets, and scheduled deliveries. B2C fulfillment primarily uses parcel carriers and last-mile delivery networks.
Regulations
B2B fulfillment must comply with retailer-specific rules, EDI standards, and contractual SLAs. B2C fulfillment focuses more on consumer protection and shipping transparency.
Cost structure
B2B fulfillment costs are driven by storage, labor efficiency, freight optimization, and compliance management. B2C fulfillment costs emphasize speed, packaging, and returns handling.
Fulfillment speed
Speed matters in B2B fulfillment, but reliability and accuracy are often more important than same-day shipping. Missed delivery windows can disrupt entire retail supply chains.
Best practices for B2B fulfillment integration
Seamless integration is the backbone of scalable b2b order fulfillment services.
Standardize data exchange across systems
Using standardized data formats such as EDI reduces manual intervention and ensures consistent communication between partners.

Integrate fulfillment systems with core business platforms
Connecting WMS platforms with ERP and CRM systems enables real-time visibility into orders, inventory, and customer relationships.
Synchronize inventory across all locations
Centralized inventory syncing prevents allocation conflicts and supports multi-warehouse fulfillment strategies.
Design storage for high-density inventory
B2B fulfillment requires storage layouts optimized for pallets, cases, and bulk handling to maximize space efficiency.
Route orders based on logic and constraints
Logic-based routing ensures orders are fulfilled from the most cost-effective location while meeting delivery requirements.
Validate compliance during fulfillment
Compliance checks during picking and packing reduce costly errors and chargebacks.
Test workflows end to end
Comprehensive testing with fulfillment partners ensures systems perform reliably before scaling volume.
Monitor KPIs in real time
Key metrics such as order accuracy, on-time delivery, inventory turnover, and exception rates provide actionable insights for continuous improvement.
5 tips to improve the B2B fulfillment process
Improving b2b fulfillment performance requires both operational discipline and technology investment.
First, automate order processing to reduce manual errors and accelerate throughput. Automation improves consistency and scalability.
Second, implement robust inventory management systems to maintain accurate stock levels and support demand forecasting.
Third, optimize packaging and shipping strategies to protect products and control freight costs through carrier negotiations.
Fourth, prioritize customer satisfaction by maintaining transparent communication and proactively resolving fulfillment issues.
Finally, continuously analyze performance data using KPIs to identify inefficiencies and optimize workflows over time.
B2B fulfillment FAQs
What is the difference between B2B and B2C fulfillment?
B2B fulfillment focuses on bulk orders, freight shipping, and retailer compliance, while B2C fulfillment prioritizes speed, parcel delivery, and consumer experience.
Can I handle B2B fulfillment in-house?
Yes, but in-house fulfillment becomes challenging as order volume and compliance requirements increase. Many growing businesses outsource to reduce complexity.
How can B2B fulfillment services help improve my supply chain?
Professional B2B fulfillment services provide technology, expertise, and infrastructure that improve accuracy, reduce costs, and enhance scalability.
Is B2B fulfillment only for large businesses?
No. Small and mid-sized businesses increasingly use outsourced B2B fulfillment to enter wholesale markets without heavy upfront investment.
What is B2B fulfillment and how is it different from B2C?
B2B fulfillment ships products to businesses under contractual agreements, while B2C fulfillment ships directly to consumers with a focus on speed and convenience.
How to manage inventory for B2B fulfillment?
Inventory should be managed in bulk units with real-time visibility and integrated forecasting tools to support recurring orders.
What are B2B fulfillment strategies for recurring orders?
Recurring orders benefit from automated replenishment, contract-based pricing, and reserved inventory allocations.
What are the key components of the B2B fulfillment process?
Order processing, inventory management, picking and packing, shipping and delivery, and returns management form the core components.
Conclusion
B2B fulfillment is no longer a back-office function. It is a strategic capability that influences revenue stability, partner relationships, and growth potential. Businesses that invest in optimized b2b fulfillment operations gain a competitive edge through accuracy, compliance, and scalability.
Whether managed in-house or outsourced to specialized partners, the right B2B fulfillment strategy enables businesses to meet retailer expectations, control costs, and scale with confidence in an increasingly complex supply chain landscape.