Since you don’t need to buy products in advance or manage storage, dropshipping is especially appealing to new ecommerce sellers, solo founders, and entrepreneurs who want to launch or grow an online store with minimal upfront capital. That said, dropshipping also comes with trade-offs, including less control over product quality, branding, packaging, delivery speed, and the overall customer experience.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- The key advantages and disadvantages of dropshipping
- What dropshipping is and how it works
- How does dropshipping work?
- How to start dropshipping
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of how dropshipping works, whether it’s a good fit for your business goals, how to avoid common pitfalls, and which alternative models might help you reduce risk, cut costs, or streamline operations.
What is Dropshipping?
Dropshipping is an e-commerce business model that allows you to sell products online without holding inventory. The supplier handles storage and shipping, while you earn the difference between the retail price and the wholesale cost.
In a dropshipping business, you list products for sale on your online store without purchasing them in advance. When a customer places an order, you buy the product from a third party supplier, usually a manufacturer or wholesaler. That supplier then ships the product directly to the customer on your behalf. Your profit comes from the margin between what the customer pays and what you pay the supplier.
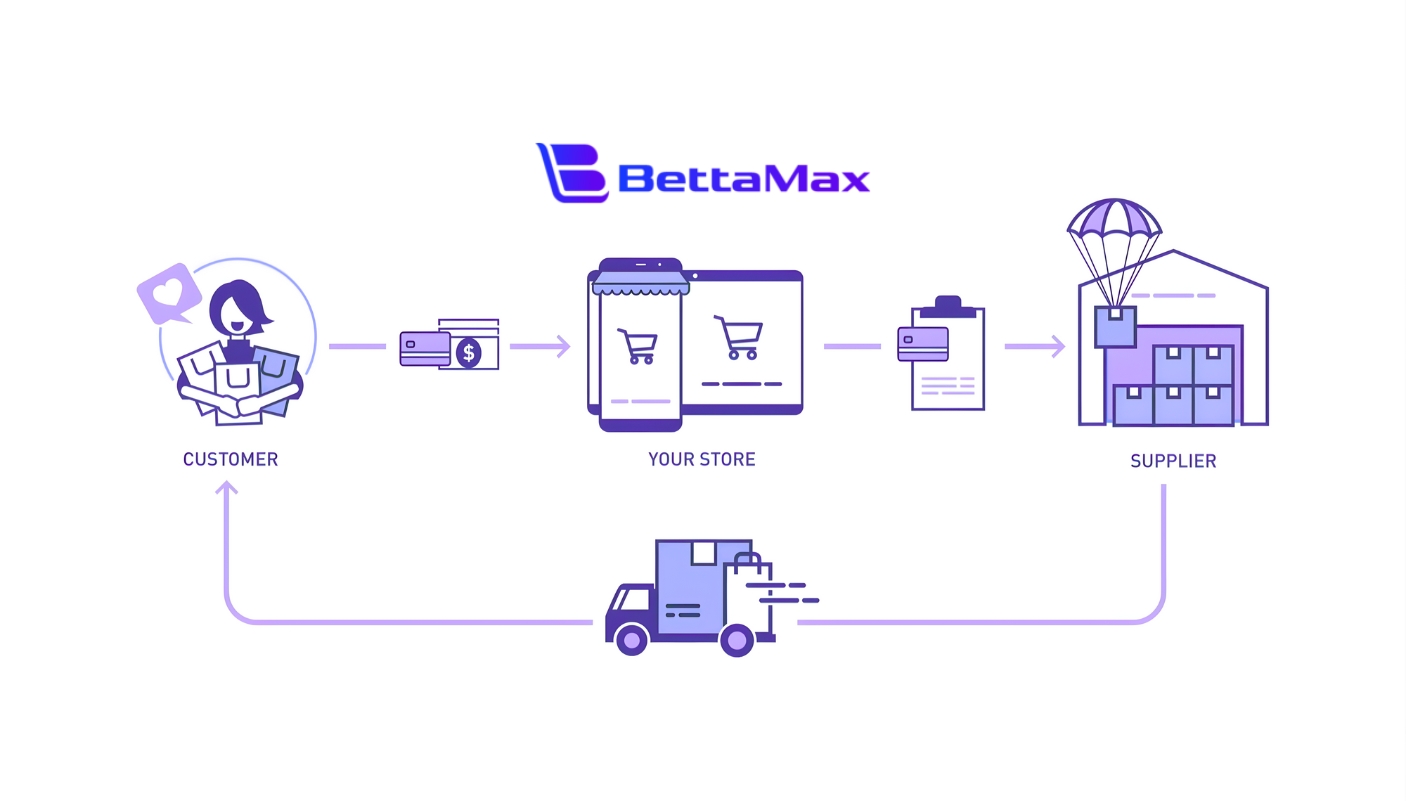
This model is popular because it requires low startup capital and removes the need for inventory management, warehousing, or in house fulfillment. As a result, dropshipping is often chosen by ecommerce beginners, solo founders, and businesses that want to test products or enter new markets with minimal financial risk. There are some keytake aways for this bussiness model:
- Buy low, sell high as a middleman
- You never own inventory before a sale happens
- Suppliers ship directly to the customer
- Profit comes from the margin, not the product
- Dropshipping is primarily an inventory model
However, relying on third party suppliers also means less control over important parts of the business. Product quality, packaging, shipping speed, and branding are largely outside the seller’s direct control, which can affect customer experience and long term brand credibility.
What is a dropshipper?
A dropshipper is the person or business that sells products online without keeping them in stock. Instead of holding inventory, the dropshipper acts as a middleman between the customer and the supplier.

When a customer places an order, the dropshipper collects the payment, forwards the order details to a third party supplier, and pays the wholesale price. The supplier then ships the product directly to the customer. The dropshipper earns a profit from the difference between the retail price charged to the customer and the cost paid to the supplier.
In practice, a dropshipper is responsible for:
- Choosing products and setting retail prices
- Building and managing the online store or sales channel
- Marketing, advertising, and driving traffic
- Handling customer service, returns, and refunds
The supplier handles:
- Inventory storage
- Order fulfillment and shipping
How does the Dropshipping Model work?
At a high level, dropshipping is a fulfillment model where the seller never physically handles the product. Instead of stocking inventory, the seller focuses on running an online store, while third party suppliers manage storage, packing, and shipping.
The dropshipping model works by selling products first and purchasing them from a supplier only after a customer places an order, with the supplier shipping directly to the customer.
How dropshipping works in basic steps:
- A customer places an order on the seller’s online store.
- The seller forwards the order details and payment to a third party supplier.
- The supplier packs and ships the product directly to the customer.
- The seller confirms shipment and provides customer support as needed.
In most cases, the supplier does not communicate directly with the customer. This means the seller remains responsible for customer service, including order updates, returns, refunds, and exchanges.
If issues arise such as delays, damaged products, returns, or refunds, the seller typically handles customer support and coordinates with the supplier behind the scenes. Some suppliers may assist with returns, but the seller is usually the primary point of contact for the customer.
Types of Dropshipping Models
Dropshipping is not a single, fixed business model. In practice, there are several types of dropshipping models, each with different levels of control, risk, profit margins, and operational complexity. Understanding these models helps you choose the right approach based on your goals, budget, and experience.
1. Product reselling dropshipping
This is the most common dropshipping model. You sell ready made products from manufacturers or wholesalers without making any changes to the product itself.
You list existing products in your store, set your own prices, and market them to customers. When an order is placed, the supplier ships the product directly to the customer.
This model is easy to start and requires minimal upfront investment, but competition is often high and profit margins can be thin.
2. Print on demand dropshipping
Print on demand is a variation of dropshipping where products are customized only after a customer places an order. Common examples include T shirts, hoodies, mugs, posters, and phone cases.
You create designs and upload them to a print provider. When a customer orders, the provider prints the design, fulfills the order, and ships it to the customer.
This model offers more branding control and differentiation, but production costs are usually higher than standard reselling.
3. Private label dropshipping
Private label dropshipping allows you to sell products under your own brand while still outsourcing fulfillment.
Instead of selling generic products, you work with a supplier who can add your logo, custom packaging, or branded inserts. The supplier ships orders directly to customers under your brand name.
This model offers stronger brand identity and higher perceived value, but often requires higher minimum order quantities or setup costs.
4. Supplier marketplace dropshipping
In this model, you source products from large supplier marketplaces such as AliExpress, Alibaba, or specialized dropshipping platforms.
These marketplaces provide access to thousands of products and suppliers in one place, making it easy to test products quickly. However, product quality and shipping times can vary widely depending on the supplier.
5. Domestic supplier dropshipping
Domestic dropshipping focuses on suppliers located in the same country as your target market.
For example, selling to US customers using US based suppliers allows for faster shipping times and easier returns. This model improves customer experience but usually comes with higher product costs and lower margins.
6. High ticket dropshipping
High ticket dropshipping is a dropshipping model that focuses on selling high priced products rather than high volume, low cost items. Instead of relying on dozens or hundreds of small orders, this model generates revenue from fewer sales with a much higher average order value.

Typical high ticket dropshipping products include large, complex, or premium items that customers research carefully before buying, such as:
- Furniture
- Home appliance
- Consumer electronics
- Fitness and sports equipment
- Outdoor and recreational products
- Specialized or professional equipment
Because each sale can generate significant revenue, high ticket dropshipping typically relies on fewer transactions to reach profitability. However, customers tend to take longer to make purchasing decisions, which results in longer sales cycles and a greater need for detailed product information, trust signals, and responsive customer support.
This model also places a stronger emphasis on customer experience. Buyers expect accurate descriptions, reliable shipping, clear return policies, and professional communication. As a result, successful high ticket dropshipping businesses often invest more in supplier vetting, branding, and post purchase support compared to traditional low ticket dropshipping stores.
Pros and Cons of Dropshipping
Dropshipping is often promoted as an easy way to start an online business, but like any business model, it comes with clear advantages and trade offs. Before deciding whether dropshipping is right for you, it’s important to understand both the benefits and the limitations of this model.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Is Dropshipping Legal and Legit?
Yes, dropshipping is legal and legitimate in most countries, including the United States, as long as it is run in compliance with applicable laws and platform policies.
From a legal standpoint, dropshipping is simply a method of order fulfillment, not an illegal business activity. Many traditional retailers have used similar direct shipping arrangements for decades. However, legality depends on how the business is operated, not on the dropshipping model itself.

To run a legitimate dropshipping business, sellers must:
- Sell products they are legally allowed to resell
- Avoid counterfeit, copyrighted, or trademark infringing products
- Provide accurate product descriptions and pricing
- Follow consumer protection and refund laws
- Comply with tax obligations, including sales tax where applicable
Dropshipping is also considered legitimate by major ecommerce platforms and marketplaces such as Shopify, Amazon, Etsy, and eBay, provided sellers follow each platform’s specific dropshipping policies.
Read more: Is Amazon Dropshipping Legal? (Updated 2026)
That said, dropshipping can become illegal or unethical if sellers mislead customers, sell fake or restricted products, or ignore tax and consumer protection requirements. In these cases, the issue is not the dropshipping model itself, but poor business practices.
Dropshipping vs Other eCommerce Business Models
When starting an online business, choosing the right ecommerce model is just as important as choosing the products you sell. Dropshipping is often compared with other popular ecommerce models because each approach differs in terms of cost, risk, control, and scalability. The table below highlights the key differences between dropshipping and other common ecommerce business models to help you decide which option best fits your goals and resources.
| Criteria | Dropshipping | Amazon FBA | Private Label | Wholesale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inventory ownership | No inventory | Inventory stored at Amazon | Seller owned inventory | Seller owned inventory |
| Upfront investment | Very low | Medium to high | High | High |
| Order fulfillment | Supplier handles shipping | Amazon handles fulfillment | Seller or third party logistics | Seller or third party logistics |
| Branding control | Limited | Limited | Full control | Moderate |
| Profit margins | Low to medium | Medium | High | Medium |
| Ease of starting | Very easy | Easy to moderate | More difficult | More difficult |
| Scalability | Easy to scale | Easy to scale | Moderately scalable | Moderately scalable |
| Risk level | Low | Medium | High | High |
Is Dropshipping Profitable in 2026?
The short answer is yes, dropshipping can still be profitable in 2026, but it is no longer a “get rich quick” business model. Profitability depends on how well you manage costs, choose products, build trust, and differentiate your store in an increasingly competitive ecommerce landscape.
Why dropshipping can still be profitable?
Dropshipping continues to attract sellers because of its low barrier to entry. You do not need to invest heavily in inventory, warehouses, or logistics, which reduces financial risk and makes it easier to test products and niches.
In 2026, profitability is often driven by smarter product selection, faster shipping options, and better customer experience rather than simply copying trending products. Sellers who focus on problem solving products, niche markets, or higher average order values tend to perform better.
Realistic profit margins in 2026
Most dropshipping stores operate on net profit margins between 5 percent and 20 percent, depending on the niche, supplier, and traffic source.
- Low ticket products usually have thinner margins but higher order volume
- High ticket dropshipping can generate larger profits per sale but requires stronger trust and longer sales cycles
- Branded or private label dropshipping often achieves higher margins due to better differentiation
Advertising costs, payment processing fees, refunds, and taxes all directly impact final profitability.
Product selection: Winning products solve real problems, have clear demand, and are difficult to find locally. Generic products with heavy competition are harder to profit from.
Traffic acquisition costs: Paid ads are more expensive than in previous years. Profitable stores optimize creative, use multiple channels, and combine paid traffic with organic sources like SEO or email.
Shipping speed and reliability: Customers in 2026 expect faster delivery. Using US based or regional suppliers can significantly improve conversion rates and reduce refunds.
Brand trust and positioning: Stores that look professional, offer clear policies, and provide responsive customer support convert better and experience fewer chargebacks.
What works best in 2026
In 2026, profitable dropshipping businesses tend to focus on:
- Niche specific stores instead of general stores
- Higher quality suppliers and faster fulfillment
- Content driven traffic (such as SEO, short form video, and email marketing)
- Long term brand building rather than one off product launches
Dropshipping is still profitable in 2026 for sellers who adapt to market changes, control costs, and focus on customer experience. It rewards strategic thinking and execution, not shortcuts or copy paste tactics.
FAQs about Dropshipping for Business
1. Is dropshipping still worth it in 2026?
Yes, dropshipping is still worth it in 2026 if it is treated as a real business. Sellers who focus on niche markets, reliable suppliers, faster shipping, and strong customer experience can still build profitable stores.
2. How much money can you make with dropshipping?
Earnings vary widely. Some beginners make a few hundred dollars per month, while established stores can generate thousands in profit. Net profit margins typically range from 5 percent to 20 percent, depending on costs and pricing strategy.
3. Do you need money to start dropshipping?
Yes, but the startup cost is relatively low. You may need a small budget for a website, apps, product samples, and initial marketing, but you do not need to buy inventory upfront.
4. Is dropshipping legal in the United States?
Yes, dropshipping is legal in the US as long as you follow business laws, tax regulations, and platform policies. Selling counterfeit or trademarked products without permission is illegal.
5. Do you need an LLC to start dropshipping?
No, you do not need an LLC to start. However, many sellers form an LLC later to separate personal and business finances and add credibility.
6. How long does it take to see results with dropshipping?
Some sellers see results within weeks, while others take several months. Success depends on product selection, marketing skills, and consistent testing and optimization.
Final Thoughts
Dropshipping is a flexible ecommerce model that continues to attract sellers because of its low upfront investment and simple operations. While it comes with certain limitations, it can still be a practical option for those looking to start or experiment with online selling.
As with any business model, results depend on planning, execution, and consistency. Understanding how dropshipping works and its trade offs can help you decide whether it fits your goals and resources.








