For growing ecommerce brands, understanding What is a fulfillment center is the first step to improving delivery speed and reducing operational pressure, since these facilities manage storage, order processing and shipping in one streamlined workflow.
Explore how fulfillment centers work and why they matter together with BettaMax.
What is a fulfillment center?
Definiton of fulfillment center
According to Cambridge Dictionary, a fulfillment center is a place where goods are stored, packed, and sent to customers who have ordered them. In the modern ecommerce landscape, fulfillment centers serve as specialized facilities designed to handle the complete order fulfillment process from receiving inventory to delivering products to end customers.
To understand how fulfillment progress is shown to customers, read our guide on what does fulfillment status mean.

Understanding what is a fulfillment center also requires recognizing how it differs from traditional long-term storage warehouses. Unlike traditional warehouses that primarily focus on long term storage, fulfillment centers are optimized for speed and efficiency. They process individual customer orders daily, managing everything from inventory management to returns processing. This operational model makes them essential infrastructure for ecommerce brands seeking to scale without building their own logistics operations.
Real world fulfillment center examples
Major fulfillment center operators include Amazon with its extensive FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) network, ShipBob serving small to medium ecommerce businesses, Shopify Fulfillment Network integrated with Shopify stores, and specialized 3PL providers like Deliverr and ShipMonk. These facilities range from 100,000 square foot regional centers to massive 1 million square foot mega centers strategically positioned near major population centers. These real-world models clearly illustrate what is a fulfillment center across different business sizes.
Read more: What is 3PL? The Complete Guide to Third-Party Logistics

Fulfillment centers typically operate 24/7 during peak seasons, processing thousands of orders daily with advanced warehouse management systems, automated picking technology, and direct carrier integrations for seamless shipping.
Key components of a modern fulfillment center
Modern fulfillment facilities incorporate several critical components. The receiving area handles incoming inventory from manufacturers and suppliers. Storage zones organize products using systematic SKU management and bin locations.
Picking areas where workers or robots retrieve items from storage shelves. Packing stations equipped with shipping materials and label printers. Shipping docks with direct carrier access for rapid dispatch. Returns processing zones for inspecting and restocking returned merchandise. Quality control stations ensuring order accuracy before shipment.
Advanced fulfillment centers also include climate controlled sections for sensitive products, hazmat storage for regulated items, and kitting areas for product bundling and custom packaging services.
Benefits of using a fulfillment center
Faster shipping and delivery times
Once you understand what is a fulfillment center, the advantages become much clearer for scaling ecommerce operations. Fulfillment centers strategically located near your customers enable same day or next day delivery options. With inventory distributed across multiple geographic locations, you can reduce shipping zones and transit times.
Professional fulfillment partners typically ship orders within 24 hours of receiving them, compared to 2 to 3 days for many in-house operations. This speed advantage directly impacts customer satisfaction and repeat purchase rates.
Reduced operational costs
Outsourcing fulfillment eliminates the need for warehouse leases, utilities, equipment purchases, and hiring warehouse staff. You pay only for the space and services you actually use, converting fixed costs into variable costs that scale with your business.
Fulfillment centers leverage economies of scale to negotiate better shipping rates than individual businesses can obtain. Most brands save 15% to 30% on total fulfillment costs by outsourcing to specialized providers.
Scalability for business growth
Fulfillment centers provide instant capacity during peak seasons without requiring you to hire temporary staff or lease additional space. Whether you ship 100 orders monthly or 10,000 professional fulfillment partners adjust resources to match your volume.
This flexibility allows you to test new markets, launch seasonal products, or handle viral growth without logistics constraints holding you back.
Access to advanced technology and automation
Professional fulfillment centers invest millions in warehouse management systems, inventory tracking software, automated picking robots, and carrier integrations. These technologies would be cost prohibitive for individual ecommerce businesses to implement.
You gain access to real time inventory visibility, automated order routing, predictive analytics, and seamless integration with your ecommerce platform without capital investment.
How do fulfillment centers work
To move orders quickly and accurately, fulfillment centers follow a structured workflow that begins the moment inventory arrives and continues until a package reaches the carrier. Here’s how each step works behind the scenes.
Step 1: Receiving and inventory storage
When you ship inventory to a fulfillment center, the receiving team scans and inspects each item, verifying quantities against your shipment manifest. Products are assigned storage locations based on size, weight, velocity, and special handling requirements.
The warehouse management system creates a digital map of where every SKU is located. High velocity items are positioned closer to packing stations for faster picking.
If you often see the label awaiting fulfillment, this separate guide explains exactly what it means and why orders stay in that stage.
Step 2: Order processing and picking
When a customer places an order on your website, the order data automatically transmits to the fulfillment center’s system. The warehouse management system generates a pick list optimized for the most efficient route through the warehouse.
Warehouse workers or automated robots retrieve the items from their storage locations. Barcode scanning at each step ensures accuracy and updates inventory counts in real time.

Step 3: Packing and quality control
Retrieved items arrive at packing stations where workers select appropriate box sizes, add protective materials, and include any branded inserts or promotional materials you’ve provided.
Each order goes through a final verification scan to confirm all items are correct before sealing. Shipping labels are automatically generated with the optimal carrier and service level based on destination, package weight and your shipping rules.
Step 4: Shipping and last mile delivery
Packed orders are sorted by carrier and consolidated for pickup. Major fulfillment centers have direct relationships with USPS, UPS, FedEx, and regional carriers, often with multiple daily pickups.
Tracking information automatically uploads to your ecommerce platform and triggers customer notification emails. The fulfillment center handles any carrier issues, damaged packages or delivery exceptions.
Step 5: Returns management
When customers initiate returns through your store, the fulfillment center receives the returned merchandise, inspects it for condition, and determines whether items can be restocked or need to be disposed of.
Inventory counts update automatically, and the warehouse management system can trigger refund notifications to your ecommerce platform. Some fulfillment centers offer advanced returns processing including product testing, repackaging, or liquidation services for damaged goods.
What is the different between Fulfillment Center vs Warehouse
Many businesses confuse fulfillment centers with warehouses, yet each serves a very different purpose. Knowing how they differ helps you choose the right solution for your storage, shipping needs and customer expectations. See the comparison below, this comparison further clarifies What is a fulfillment center and when businesses should choose one
Detailed comparison of fulfillment center vs warehouse
| Feature | Fulfillment center | Warehouse |
| Primary function | Process and ship individual customer orders | Long term bulk storage |
| Order volume | High volume, small orders daily | Low volume, large shipments |
| Typical storage duration | 30 to 90 days (fast turnover) | 90 days to 12+ months |
| Value added services | Picking, packing, shipping, kitting, returns | Receiving, storage only |
| Technology level | Advanced WMS, automation, integrations | Basic inventory tracking |
| Location strategy | Near population centers for fast shipping | Near manufacturing or distribution hubs |
| Cost structure | Per order + storage fees | Primarily storage fees |
| Best for | Ecommerce brands shipping direct to consumers | Wholesale distributors, bulk storage needs |
Which one does your business need
Choose a fulfillment center if you sell direct to consumers online, ship individual orders daily, need fast delivery times, want to outsource logistics operations, or require value added services like custom packaging and returns management.
Choose a warehouse if you primarily serve wholesale customers, ship large quantities to retailers, have slow inventory turnover, need long term storage only, or have specialized storage requirements without needing order fulfillment services.
Fulfillment center vs distribution center
Many teams confuse fulfillment centers with distribution centers because both move products through the supply chain. Yet their workflows, customers and speed are very different.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right model for your operational needs.
Detailed comparison of fulfillment center vs distribution center
| Feature | Fulfillment center | Distribution center |
| End customer | Individual consumers (B2C) | Retail stores and businesses (B2B) |
| Order size | Single units or small quantities | Cases, pallets, bulk quantities |
| Shipping method | Parcel carriers (UPS, FedEx, USPS) | LTL freight, full truckloads |
| Processing speed | Same day to 24 hours | 2 to 5 days |
| Geographic coverage | Multiple locations for fast delivery | Regional hubs serving large territories |
| Inventory mix | Thousands of SKUs in small quantities | Fewer SKUs in larger quantities |
| Technology focus | Ecommerce platform integration | EDI, supply chain systems |
| Best for | Online retailers, direct to consumer brands | Manufacturers, wholesale distributors, retail chains |
Which one does your business need
The comparison shows that fulfillment centers are built for speed, small parcel shipping and direct-to-consumer ecommerce, while distribution centers specialize in large-scale B2B replenishment.
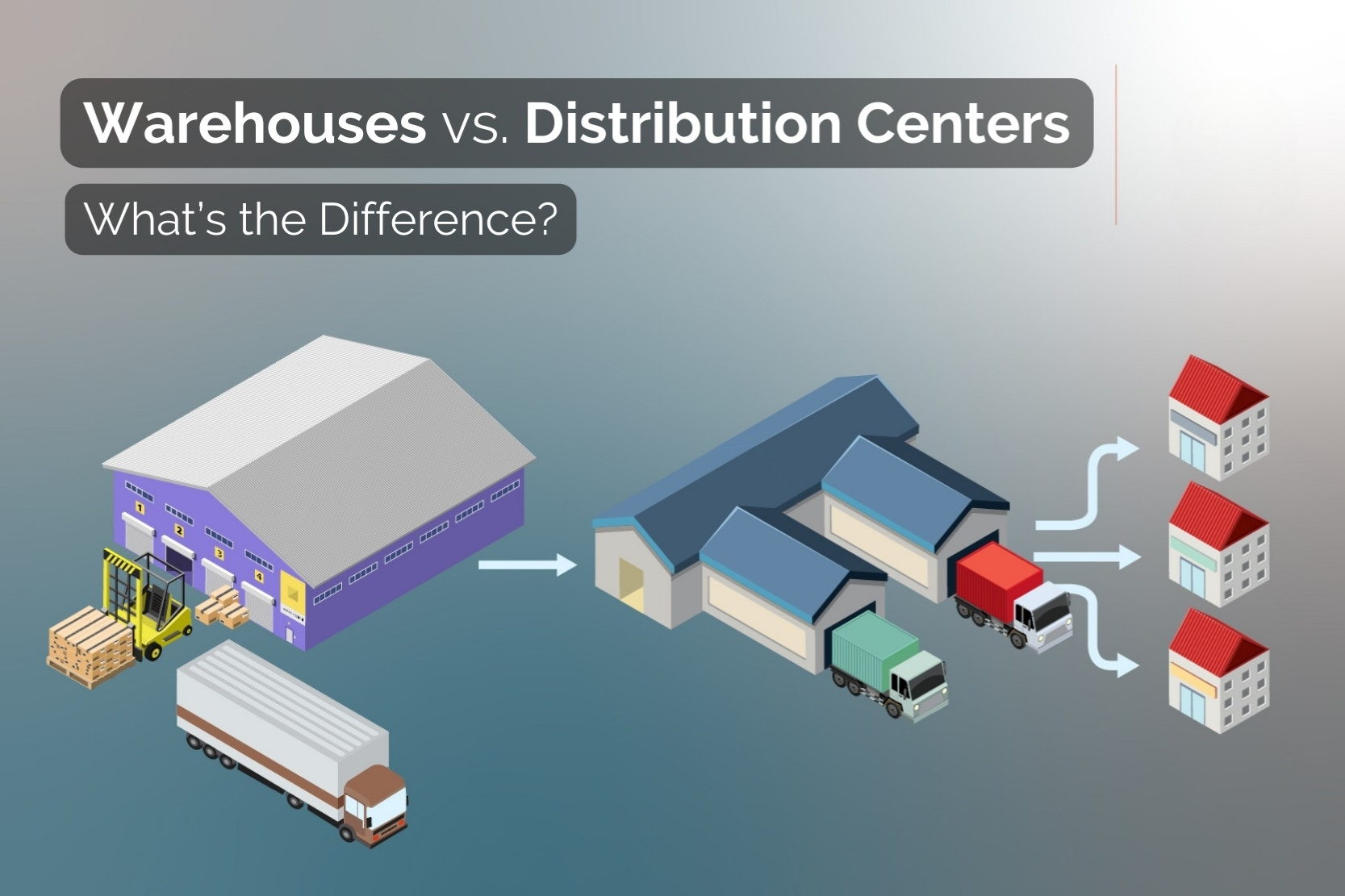
If your priority is fast order turnaround and individual deliveries, a fulfillment center is the better fit. If you ship bulk quantities to retailers or manage upstream supply chain flows, a distribution center is more suitable.
How to choose a fulfillment partner for your ecommerce business
Evaluate location and shipping coverage
Check if warehouses are positioned near your customers. Multi location networks reduce shipping costs and enable faster delivery. Request zone analysis showing delivery timeframes to your customer base from each location.
Assess technology integration capabilities
Verify seamless integration with your ecommerce platform (Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce). Integration should update inventory, orders, and tracking automatically in real time. Test thoroughly before launch.
Review pricing structure and hidden fees
Get complete pricing including receiving, storage, pick and pack, kitting and returns fees. Watch for hidden costs like setup fees and minimum commitments. Calculate total cost per order to compare accurately.

Check service level agreements and performance metrics
Review order accuracy rates, shipping cutoffs, and inventory accuracy standards. Professional partners should offer 99.5%+ accuracy and same day shipping. Request performance data from existing clients.
Examine customer support and communication
Evaluate communication channels and account management options. Test responsiveness during sales process. Ask for references from similar businesses to understand real world support quality.
Top 4 technology in modern fulfillment centers
Warehouse management systems (WMS)
WMS platforms orchestrate all warehouse operations from receiving to shipping. They track inventory locations, optimize picking routes, manage labor, and generate shipping labels. Advanced systems use machine learning to predict demand and identify slow moving inventory.
Automation and robotics
Modern centers use automated guided vehicles for transport, robotic picking arms for retrieval, and conveyor networks between stations. Amazon operates over 520,000 robotic units alongside human workers to increase speed and accuracy.
Real time inventory tracking
RFID tags and barcode scanning capture every transaction automatically. Cloud systems sync data across warehouses and your store in real time, preventing overselling and enabling better forecasting through web or mobile dashboards.

Integration with ecommerce platforms
Pre built integrations with Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce and Magento automatically transmit orders, update inventory across channels, and push tracking information. This eliminates manual entry and keeps customers informed throughout fulfillment.
Conclusion
By clearly understanding what is a fulfillment center, businesses can decide when outsourcing logistics will elevate efficiency, strengthen customer satisfaction and create a scalable foundation for long-term ecommerce growth.








