The question “how much do dropshippers make” is asked by thousands of aspiring entrepreneurs exploring this business model. The answer isn’t simple because dropshipping income varies dramatically based on niche, marketing strategy, supplier relationships, and operational efficiency. Some dropshippers earn zero while others generate six-figure annual incomes.
This guide breaks down real dropshipping income data, explains the factors influencing earnings, and reveals strategies successful dropshippers use to maximize profits. You’ll learn exactly how much do dropshippers make per week, month, and year, plus actionable steps to increase your own dropshipping income.
Understanding the dropshipping business model
Dropshipping operates on a straightforward principle: you act as a middleman between suppliers and customers. When a customer purchases from your store, you buy the product from a supplier at wholesale price and have it shipped directly to the customer. You keep the difference as profit.
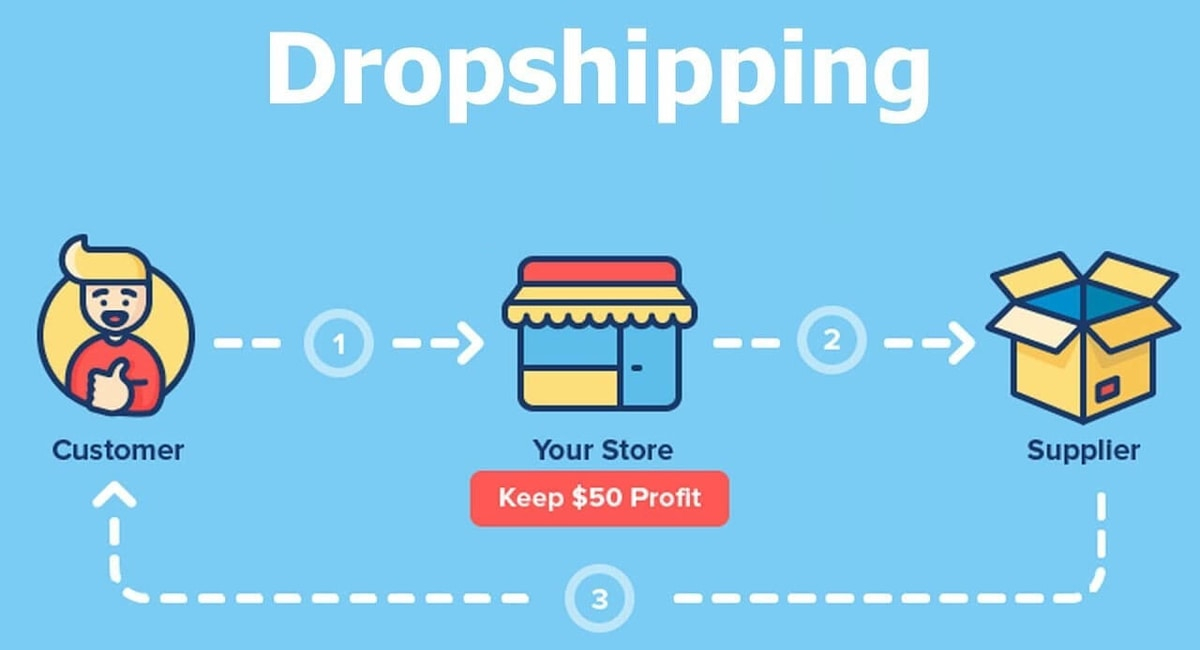
The financial mechanics appear simple, but success requires mastering several interconnected variables. Your profit depends on product selection, supplier pricing, marketing efficiency, operational automation, and customer retention. Failing at any single variable crushes profitability.
Unlike traditional retail where you purchase inventory upfront, dropshipping requires capital only after customers place orders. This eliminates inventory risk but creates tight cash flow management challenges. A successful dropshipping business generates revenue faster than expenses, creating positive cash flow that funds growth.
How profitable is dropshipping?
Dropshipping profitability isn’t guaranteed but is absolutely achievable with proper execution. The challenge isn’t whether dropshipping can be profitable but rather whether you have the skills, patience, and resources to make it work.
Profitability hinges on strategic positioning rather than just markup percentages. Many dropshippers obsess over adding 50% markups to products, but this approach fails if you can’t differentiate your offering. A 50% markup on a commodity product (basic phone case, generic gadget) means nothing if competitors undercut your price by 10%.
Successful dropshipping focuses on building differentiation through brand positioning, superior customer experience, or solving specific customer problems. When customers perceive genuine value beyond price, they’re willing to pay premium prices. This perception drives profitability far more than simple markup math.

Consider two dropshippers selling ergonomic office chairs. Dropshipper A marks up 20% and competes on price. Dropshipper B marks up 40% but invests heavily in content explaining back pain prevention, productivity benefits, and features. Which generates higher profit? Dropshipper B, because their marketing transforms an office chair from commodity into wellness solution. Customers pay premium prices for solutions to their problems.
The profitability difference between struggling and thriving dropshippers isn’t 20% vs 50% markups. It’s 15% effective profit margins competing on price versus 35% profit margins built on brand positioning and customer perceived value.
How to calculate dropshipping profit
Understanding your profit structure is essential for making business decisions. Here’s the calculation framework:
Revenue = Total sales from customers
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) = What you pay suppliers for products
Gross Profit = Revenue minus COGS
Marketing & Advertising Spend = What you spend on Facebook, TikTok, Google Ads, influencer partnerships
Operating Expenses = Platform fees, payment processing fees, email software, accounting tools, customer service costs
Net Profit = Gross Profit – Marketing & Advertising – Operating Expenses
Example calculation:
- Monthly revenue: $10,000 (200 orders at $50 average)
- COGS: $4,000 (40% of revenue)
- Gross profit: $6,000
- Marketing spend: $2,000
- Operating expenses: $500
- Net profit: $3,500 (35% profit margin)
Read more: How to Calculate Fulfillment Cost Per Order: A-Z Guide

This example shows how a $10,000 monthly revenue dropshipping business generates $3,500 monthly profit ($42,000 annually). Many dropshippers generate significantly less because their marketing spend or operational costs exceed these benchmarks. Others generate significantly more through better supplier relationships, higher margins, or more efficient marketing.
5 key factors influencing dropshipping income
Product and niche selection
Your product choice determines profit potential more than any other factor. Products vary dramatically in margins, competition, customer acquisition difficulty, and return rates.
High-margin niches (cosmetics, jewelry, fitness supplements) tolerate markups of 50-100% because customer decisions rely heavily on branding and brand loyalty. Customers willingly pay $30 for branded skincare that costs $5 to produce because they trust the brand.
Commodity niches (basic electronics, generic apparel, simple gadgets) tolerate markups of only 15-25% because customers compare prices and choose based on lowest cost. These niches require high volume to be profitable.

Niche focus dramatically affects profitability. Targeting “office products” broadly creates competition from Amazon, Staples, and 1,000 dropshippers. Targeting “standing desk accessories for remote workers” reduces competition 90%. Lower competition means higher margins and lower customer acquisition costs.
Product quality directly impacts profitability through reduced returns, higher reviews, repeat purchases, and positive word-of-mouth. A $50 product with 10% return rate generates $5 loss per sale. The same product with 2% return rate saves $4 per sale. Across 100 sales, quality saves $400 in losses; 8% profit improvement.
Marketing and sales strategy
Marketing efficiency determines whether dropshipping becomes profitable. A business generating $10,000 monthly revenue that spends $8,000 on marketing generates $2,000 profit (20%). The same business spending $2,000 on marketing generates $8,000 profit (80%).
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the metric controlling profitability. If your product sells for $50 with 40% COGS and 10% operating expenses, you can afford approximately $6 customer acquisition cost while maintaining profitability. Exceeding this eliminates profits.
Successful dropshippers achieve CAC of $2-$5 per customer through a combination of paid ads (Facebook, TikTok, Google), organic content marketing, email marketing, and word-of-mouth. They spend heavily on testing to find profitable channels, then scale winners ruthlessly.
Brand positioning enables premium pricing. A “luxury wellness company” can charge $45 for a water bottle that costs $8. A “generic outdoor store” can charge $15 for the same water bottle. The difference: one built brand identity; the other didn’t.
Pricing strategy affects profitability through volume and margin trade-offs. Testing price increases ($45 to $50 on a $15 product) often increases profit despite lower volume because the margin gain exceeds volume loss.
Operations and supplier relationships
Supplier choice determines operational success or failure. Unreliable suppliers create stockouts, shipping delays, quality issues, and customer complaints. These problems destroy profit margins through high refund rates, negative reviews, and lost customers.
Shipping costs directly impact net profit. A $2 difference in shipping cost on 100 monthly orders equals $200 profit difference. Negotiating supplier shipping terms, using regional fulfillment centers, or optimizing package weight matters significantly.

Operational efficiency through automation separates profitable operators from struggling ones. Dropshippers managing orders manually spend 20+ hours weekly on repetitive tasks. Automated systems handling order forwarding, tracking updates, and customer communications consume 2-3 hours weekly. The 17+ hour difference enables marketing, product development, or scaling.
Supplier redundancy prevents income volatility. Relying on one supplier means your income dies when they experience issues. Maintaining 2-3 suppliers per product category ensures continuity even if primary suppliers fail.
Customer experience and retention
Excellent customer service dramatically improves profitability through repeat customers and positive reviews. Repeat customers have zero acquisition cost, higher profit margins, and longer customer lifetime value (CLV).
Repeat customers spend 30-40% more over their lifetime than first-time customers. A customer buying once ($50) versus three times ($150) represents 200% more lifetime value from identical acquisition cost. Building repeat business multiplies profitability.
Customer reviews influence purchasing behavior dramatically. Stores with 50+ positive reviews convert 3-5x better than stores with zero reviews. Building review volume through excellent service accelerates growth and reduces marketing spend.
Market and competitive factors
Competition intensity determines achievable profit margins. Saturated niches with 100+ competitors allow 15-20% margins. Emerging niches with few competitors allow 40-60% margins. Market timing matters significantly.
Economic conditions affect consumer spending behavior. During recessions, customers buy fewer discretionary products and demand lower prices. During economic booms, customers buy more and tolerate premium pricing. Smart dropshippers adjust strategy based on economic conditions.

Seasonal demand fluctuations create income volatility. Summer products (fans, outdoor gear) generate peak sales July-August. Winter products (heaters, holiday items) peak November-January. Successful dropshippers manage multiple seasonal products to smooth income throughout the year.
How much do dropshippers make
How much do dropshippers make a week
Weekly earnings for dropshippers vary from zero to several thousand dollars depending on business maturity.
Beginners (Month 1-3): Most beginners generate $0-$500 weekly in their first 3 months. They’re investing time in setup, content creation, and initial marketing tests without yet achieving consistent sales.
Intermediate (Month 4-12): Intermediate dropshippers generating $500-$3,000 weekly have proven product-market fit, optimized marketing campaigns, and consistent customer flow.
Advanced (Year 2+): Advanced dropshippers managing multiple stores or highly optimized operations generate $3,000-$10,000+ weekly. Some achieve significantly higher weekly earnings.
Weekly earnings calculation: If you generate $100 in profit daily, that’s $700 weekly. Many successful dropshippers achieve $50-$100 daily profit within 6-12 months, translating to $350-$700 weekly.
How much do dropshippers make a month
Monthly dropshipping income follows patterns based on business development stage:
Months 1-3: $0-$2,000 monthly. Most beginners struggle to generate sales while learning the business.
Months 4-6: $500-$5,000 monthly. Businesses starting to gain traction, proving they understand customer acquisition and sales.
Months 7-12: $2,000-$10,000 monthly. Established businesses with proven systems, optimized marketing, and repeating customers.
Year 2+: $5,000-$50,000+ monthly. Mature businesses leveraging automation, multiple product lines, or multiple stores.

The median dropshipper generating income likely earns $1,500-$3,000 monthly after 12 months of effort. This assumes consistent work on marketing optimization and operational efficiency.
Variables affecting monthly income:
- Average order value ($20 products vs $100 products)
- Gross margin (15% vs 50% markup)
- Marketing efficiency (CAC of $2 vs $10)
- Repeat customer rate (5% vs 25%)
- Conversion rate (1% vs 3%)
A business generating 100 orders monthly at $50 AOV with 40% margins = $2,000 gross profit. After $800 marketing and $200 operating expenses = $1,000 net profit monthly.
How much do dropshippers make a year
Annual dropshipping income provides the clearest picture of earning potential:
Year 1: Most dropshippers generate $0-$20,000 annual profit. Many break even or lose money during learning phase.
Year 2: Successful dropshippers generate $20,000-$100,000 annual profit. Those who’ve optimized systems and built audiences earn higher amounts.
Year 3+: Mature businesses generate $50,000-$500,000+ annual profit. Some exceptional cases exceed $1 million.
These ranges assume dropshippers dedicate 15-30 hours weekly. Those working 5 hours weekly generate lower income; those working 40+ hours generate higher income.
Annual income is determined by consistent execution across months. A business generating $5,000 monthly profit generates $60,000 annually. Scaling that to $10,000 monthly ($120,000 annually) requires marketing optimization, product expansion, or launching additional stores.
The potential to reach six figures annually exists within 18-24 months for dedicated operators who master their niche, build strong supplier relationships, and scale marketing efficiently.
5 tips to increase your dropshipping profit margin
1. Build a strong brand and unique positioning
Brand-building enables premium pricing that commodity competition can’t match. Invest in professional product photography, consistent visual identity, and compelling brand storytelling explaining why customers should choose you.
Premium brands command 30-50% price premiums. A branded water bottle sells for $45; a generic alternative sells for $25. Same cost, different perception, dramatically different profit.
2. Optimize your marketing spend aggressively
Test multiple traffic sources (TikTok, Facebook, Google, Pinterest) and scale only the channels achieving CAC below your profitability threshold. Waste no money on underperforming channels.
Implement retargeting to show ads to website visitors who didn’t purchase. Retargeting converts 2-3x better than cold traffic, dramatically lowering overall CAC.
Use email marketing to nurture leads and promote to existing customers. Email generates highest ROI with minimal cost.
3. Focus on repeat customers and lifetime value
Build systems encouraging repeat purchases: loyalty programs, exclusive member discounts, email follow-ups suggesting complementary products, excellent customer service.

A 5% repeat customer rate generates 20% more annual revenue from same acquisition spend. A 25% repeat rate generates 100% more revenue. This multiplier effect transforms profitability.
4. Negotiate better supplier terms
Build relationships with reliable suppliers and leverage order history to negotiate volume discounts, extended payment terms, or faster shipping.
A 5% reduction in supplier cost on $50,000 annual inventory saves $2,500 annually – 5% of profit improvement.
5. Automate operational tasks ruthlessly
Identify repetitive tasks (order forwarding, tracking updates, customer inquiries) and automate them using tools, plugins, or outsourced services. Time freed enables scaling.
See our detailed guide on optimizing your dropshipping profit margin for specific tactics and tools.
Dropshipping profits FAQs
Is dropshipping a get-rich-quick scheme?
No. Dropshipping requires consistent effort, continuous optimization, and patience to build profitability. Most successful dropshippers spend 6-18 months before achieving consistent monthly profits of $2,000+. Those expecting rapid wealth should explore other models.
Dropshipping rewards disciplined execution: testing marketing channels, optimizing conversion rates, building audiences, and scaling what works. These skills take months to develop.
Is dropshipping really profitable?
Yes, dropshipping can be profitable when executed correctly. Profitability depends on niche selection, product research, supplier relationships, and marketing efficiency, not dropshipping itself.
A dropshipper selling premium fitness products to health-conscious audiences with excellent customer service often exceeds 40% profit margins. Another dropshipper selling generic gadgets competing on price often achieves only 5-10% margins.
The business model works; execution determines success. Those treating dropshipping seriously as a business (not a side experiment) achieve profitability within 12-18 months.
How long does it take to start earning from dropshipping?
Most dropshippers generate first sales within 4-8 weeks of launching. However, generating consistent monthly profits typically requires 6-18 months.
Timeline depends on marketing effectiveness and niche selection. An entrepreneur launching in a underserved niche with well-executed marketing might reach profitability in 4-6 months. A competitor in saturated niches might require 18-24 months.
The key variable is how quickly you identify and fix what’s not working. Entrepreneurs who test aggressively, measure results obsessively, and pivot quickly compress timelines. Those hoping to stumble into success extend them.
How much initial investment is required for dropshipping?
Dropshipping requires minimal upfront capital compared to traditional retail. You can start for under $50 or even free:
Many e-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce) offer 14-30 day free trials, letting you build and launch stores without initial payment. You can operate profitably within the trial period and pay platform fees from profits.
Initial marketing requires only $5-$50 daily spending. You can run profitable test campaigns on TikTok, Facebook, or Google for just $5/day and scale gradually as results prove profitable.
However, most successful dropshippers allocate $500-$2,000 initial investment for platform setup, initial marketing testing, domain registration, and tools. This investment accelerates profitability.
Conclusion
The answer to “how much do dropshippers make” is: it depends. Dropshipping income ranges from zero to six figures annually, with the median successful dropshipper earning $20,000-$50,000 annually after 12-18 months of consistent effort.
Success requires understanding profit mechanics, mastering marketing efficiency, building supplier relationships, and obsessing over customer experience. Those executing these fundamentals consistently generate sustainable income and scaling businesses.
Most importantly, dropshipping rewards entrepreneurial mindset: testing ideas, measuring results, learning from failures, and optimizing based on data. Those approaching dropshipping as serious business investment achieve profitability within 18 months. Those treating it as side experiment often never achieve meaningful income.
For comprehensive guidance on building a successful dropshipping business, see our complete dropshipping business plan guide. This resource covers strategic planning, financial projections, and implementation roadmaps for entrepreneurs serious about dropshipping success.
Start today with realistic expectations: profitability takes time, requires consistent effort, and rewards disciplined execution. The dropshippers earning substantial income didn’t get lucky; they out-executed competitors through superior marketing, customer service, and business fundamentals.








