In this guide, BettaMax outlines how B2C fulfillment works, highlights the key differences between B2C and B2B fulfillment, and explains how businesses can evaluate and select the right fulfillment partner.
What is B2C Fulfillment?
B2C fulfillment refers to the process of storing, picking, packing, and shipping individual customer orders directly to end consumers. It is most commonly used by ecommerce brands selling through platforms such as: Shopify, Amazon, Etsy, TikTok Shop, or direct-to-consumer websites. Unlike wholesale or bulk distribution, this model focuses on high order volumes with smaller quantities per order.

In a typical B2C fulfillment workflow, inventory is stored in one or multiple fulfillment centers. When a customer places an order, the system triggers picking and packing, followed by last-mile delivery through parcel carriers. Speed, accuracy, and transparency are critical, as customers expect fast delivery, real-time tracking, and hassle-free returns.
While B2C fulfillment is often discussed alongside B2B fulfillment, the two models serve fundamentally different customer journeys. Understanding these differences is essential when designing an integrated logistics strategy or deciding which model best fits your business.
5 key components of the B2C fulfillment process
In practice, the B2C fulfillment process is strongly influenced by modern consumer expectations, particularly in mature ecommerce markets such as the United States. Customers increasingly demand same-day or next-day delivery, accurate delivery windows, and transparent post-purchase communication. To meet these expectations, fulfillment operations must be optimized around speed, scalability, and operational consistency across every stage of the process.
Inventory receiving and storage
The B2C fulfillment process begins with inventory receiving and storage. Products are received at the fulfillment center, inspected for quality and quantity, and then systematically stored for fast access. Proper inbound handling ensures inventory accuracy and prevents downstream issues such as stock discrepancies or delayed order processing.

In high-volume B2C environments, especially for apparel and consumer goods, organized storage layouts and real-time inventory updates are critical to support rapid order fulfillment and minimize picking errors.
Order processing and management
Order processing starts the moment a customer places an order. This stage includes order validation, system synchronization across sales channels, and workflow prioritization within the warehouse. Efficient order management ensures that orders move quickly from checkout to fulfillment without manual intervention or data mismatches.
For subscription-based ecommerce models, order processing must also handle recurring orders, predictable shipping schedules, and inventory forecasting. When managed effectively, this component supports consistency and long-term customer retention.
Picking and packing
Picking and packing are among the most labor-intensive components of the B2C fulfillment process. Each order typically consists of one or a few items that must be picked individually, packaged securely, and prepared for shipment.

For example, a US-based apparel brand may process hundreds or thousands of small orders per day. Each order requires accurate item selection, protective packaging, branded inserts, and precise labeling. Even minor errors at this stage can lead to negative customer reviews or increased return rates, directly impacting brand perception.
Shipping and last-mile delivery
Shipping and last-mile delivery determine how quickly and reliably orders reach customers. This component includes carrier selection, shipping label generation, and coordination with parcel delivery networks.
In competitive ecommerce markets, fast and predictable delivery has become a key differentiator. Optimizing last-mile delivery helps meet customer expectations for speed while controlling shipping costs and maintaining service consistency.
Returns handling and reverse logistics
Returns handling completes the B2C fulfillment lifecycle. This stage involves receiving returned items, inspecting product condition, processing refunds or exchanges, and restocking inventory when possible.
An efficient reverse logistics process reduces operational losses and helps preserve customer trust. In B2C fulfillment, where return rates can be high, especially in fashion and lifestyle categories, streamlined returns handling is essential to maintaining profitability and customer satisfaction.
B2B Fulfillment vs B2C Fulfillment: Which Model is right for your business?
While both models involve order processing and delivery, B2B fulfillment and B2C fulfillment differ significantly in structure, scale, and operational priorities. Choosing the right model depends on how your business sells, who your customers are, and how orders are placed.

Buyer’s Journey
In B2C fulfillment, the buyer’s journey is short and transactional. Individual consumers make purchasing decisions quickly, often driven by convenience, pricing, or emotional factors. Repeat purchases are influenced heavily by delivery speed and overall experience.
In contrast, B2B fulfillment supports business buyers who place orders less frequently but in larger quantities. The sales cycle is longer, multiple stakeholders may be involved, and purchasing decisions are often governed by contracts or negotiated terms.
Order Size and Volume
B2C fulfillment typically involves small order sizes but high overall order volumes. Orders are packed in boxes or poly mailers and shipped directly to consumers’ homes. This requires efficient parcel handling and last-mile delivery optimization.
B2B fulfillment focuses on large, bulk orders shipped every few weeks or months. These shipments often require pallets, freight transportation, and delivery to warehouses or distribution centers rather than individual addresses.
Regulations and Compliance
From a compliance perspective, B2C fulfillment generally faces fewer regulatory requirements. However, it demands real-time tracking, clear shipping policies, and efficient returns management to meet customer expectations.
B2B fulfillment may require additional documentation such as EDI integration, barcodes, invoices, and compliance with stricter international shipping regulations, particularly for cross-border trade.
Technology Requirements
Technology in B2C fulfillment prioritizes ecommerce platform integration, user-friendly checkout experiences, and real-time visibility. Systems must synchronize inventory, orders, and tracking information seamlessly.

B2B fulfillment often relies on EDI systems and automated order processing to support large retailers or distributors. Efficiency and accuracy at scale are critical.
Customer Relationship
In B2C fulfillment, there are typically no formal contracts. Customers are free to purchase at any time, and loyalty is driven by experience rather than obligation.
B2B fulfillment relationships are contract-based and long-term. Relationship management, reliability, and consistency are key to securing repeat bulk orders.
Which model is right for your business?
There is no universal answer that fits every business. The choice between B2B fulfillment and B2C fulfillment depends on your business model, growth stage, and target customers.
If you are a new seller launching print-on-demand products or selling through ecommerce platforms such as Shopify, Etsy, or TikTok Shop, B2C fulfillment is usually the most suitable option. It allows flexibility, direct customer access, and lower upfront operational investment.

If your business is expanding into wholesale channels or distributing products through retail partners and dealers, B2B fulfillment becomes essential for handling large orders efficiently and maintaining stable operations.
Some companies adopt a hybrid approach, combining both models to diversify revenue streams and reduce risk. While this can unlock new growth opportunities, it requires strong operational management and a fulfillment system capable of handling both individual and bulk orders.
10 Tips to Choose the Right B2C Fulfillment Partner
Assess whether your business is ready to outsource fulfillment
Before choosing a partner, businesses should evaluate whether in-house fulfillment is limiting growth, consuming excessive time, or creating operational bottlenecks during peak seasons.
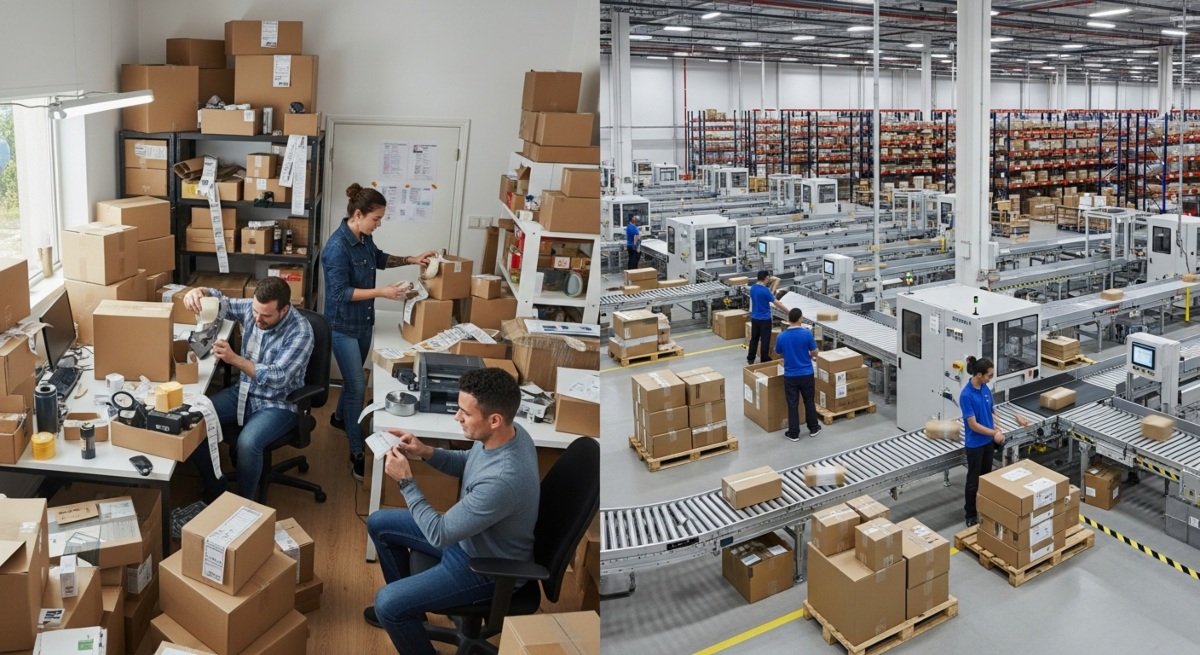

Define your core fulfillment requirements clearly
Clearly outlining must-have services such as ecommerce integrations, branded packaging, returns handling, or international shipping helps narrow down suitable fulfillment partners early in the process.
Prioritize pricing transparency and cost structure
A reliable fulfillment partner should provide clear, upfront pricing for storage, picking, packing, shipping, and additional services to avoid unexpected cost increases as order volume grows.
Evaluate warehouse locations and inventory distribution
Partners with strategically located warehouses can significantly reduce shipping times and costs, especially in markets like the United States where proximity to customers impacts delivery performance.
Choose a partner that can scale with your business
Fulfillment needs evolve as businesses grow. Selecting a partner that supports higher order volumes, new sales channels, and international expansion reduces the need for disruptive changes later.
Review technology and system integrations
Strong technology capabilities, including real-time dashboards, API access, and seamless platform integrations, are essential for maintaining visibility and control over fulfillment operations.
Ensure accurate order tracking and inventory visibility
Real-time tracking and accurate inventory reporting help prevent stockouts, overselling, and customer dissatisfaction while improving overall operational efficiency.
Consider experience in your industry or business model
A fulfillment partner with experience handling similar products or order profiles is better equipped to manage specific packaging, compliance, or handling requirements.
Evaluate service quality and communication standards
Fulfillment partners act as an extension of your brand. Proactive communication, fast issue resolution, and consistent service quality are critical for maintaining customer trust.

Verify performance through reviews and case studies
Customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies provide practical insights into a partner’s reliability, scalability, and ability to deliver consistent fulfillment performance.
7 metrics that define B2C Fulfillment success
Perfect Order Rate
Perfect Order Rate measures whether each order is delivered on time, complete, damage-free, and with accurate documentation. This metric reflects the overall reliability of B2C fulfillment operations and directly impacts customer trust and satisfaction.
Order Cycle Time
Order cycle time tracks the total duration from the moment an order is placed to when it is successfully delivered to the customer. Shorter cycle times are increasingly important as consumers expect faster shipping and real-time fulfillment performance.
Inventory Accuracy
Inventory accuracy evaluates how closely recorded stock levels match actual inventory. High accuracy ensures product availability, prevents overselling, and reduces backorders, while inaccuracies often lead to customer frustration and operational inefficiencies.
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT / NPS)
Customer satisfaction metrics such as CSAT and Net Promoter Score provide direct insight into how customers perceive the fulfillment experience. These indicators are closely linked to repeat purchases and brand reputation in B2C markets.
Customer Retention Rate
Customer retention rate measures how effectively fulfillment operations support long-term customer loyalty. Consistent delivery performance and reliable order handling encourage customers to return and continue purchasing from the brand.
Cost per Order
Cost per order assesses the total fulfillment cost associated with processing and shipping each order. This metric helps businesses understand whether operational expenses are aligned with revenue, margins, and growth objectives.
Read more: How to calculate fulfillment cost per order? Full guide & Formula

Return Rate
Return rate highlights the percentage of orders sent back by customers due to issues such as incorrect items, damage, or packaging problems. A high return rate often signals deeper fulfillment or quality control challenges that require attention.
B2C Fulfillment FAQs
How do I choose the right B2C fulfillment service for my business?
Start by defining your business needs, order volume, and customer expectations. Evaluate providers based on technology, scalability, warehouse location, service quality, and pricing transparency.
When should a brand outsource B2C fulfillment?
Outsourcing becomes beneficial when order volumes exceed in-house capacity, when faster delivery requires distributed warehouses, or when fulfillment costs become inefficient internally.
What technologies are used in B2C logistics?
Modern operations rely on warehouse management systems, order management systems, transportation management systems, barcode scanning, and API integrations with ecommerce platforms.
What KPIs measure B2C fulfillment success?
Key KPIs include order accuracy, on-time delivery rate, order cycle time, cost per shipment, return rate, and customer satisfaction metrics.
Why is order fulfillment in B2C considered difficult?
B2C fulfillment involves handling high volumes of individual orders with minimal margin for error. Customers expect speed and accuracy, and even small mistakes can lead to complaints or returns.
What are common challenges and solutions in B2C fulfillment?
Common challenges include peak season surges, inventory inaccuracies, and rising shipping costs. These can be addressed through scalable partners, data-driven forecasting, and distributed fulfillment networks.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fulfillment Strategy
B2C fulfillment is more than an operational function; it is a strategic foundation for ecommerce growth. By understanding how it differs from B2B fulfillment, selecting the right partner, and tracking the right metrics, businesses can build a fulfillment system that supports both customer satisfaction and long-term scalability.
Choosing the right model and execution approach allows brands to deliver consistently, control costs, and compete effectively in today’s fast-moving ecommerce landscape.








